

What is the best disaster recovery software in 2026? We’ve got the answer.
Disaster recovery (DR) software helps teams restore systems, data, and services after an outage. This includes things like cloud region failures, database corruption, human error, or ransomware. The goal is simple: get back online fast, with minimal data loss and operational overhead.
Below is a breakdown of the top disaster recovery tools in 2026, starting with Northflank, which offers the most complete, developer-friendly disaster recovery experience available today.
Disaster recovery (DR) is the process of restoring systems, data, and services after a failure, whether it’s a cloud outage, ransomware attack, or human error.
A disaster recovery plan defines which systems need to be restored, how quickly (RTO), how much data loss is acceptable (RPO), and who’s responsible for recovery.
Cloud disaster recovery uses cloud infrastructure to automate backups, failover, and restores across regions or providers.
Northflank is a full disaster recovery system built into a modern workload delivery platform. Schedule backups, trigger restores, fail over to healthy replicas, debug live containers, and run in your own cloud, all in one place.
Why Northflank stands out:
- Automated snapshots and native database dumps
- Scheduled backups and point-in-time restores via UI, API, or CLI
- High availability with health-checked multi-replica services
- Built-in logs, metrics, alerts, and shell access
- Supports stateless and stateful workloads
- Works in your own cloud (AWS, GCP, Azure, OCI) or on Northflank’s managed infra
- Secure by default: RBAC, mTLS, and private networking
Bottom line: If you're running modern infrastructure and want fast, testable disaster recovery without extra tooling, Northflank is the most complete platform available in 2026.
☎️ Book a demo to see how Northflank handles Disaster Recovery.
Disaster recovery (DR) refers to the process of restoring infrastructure and application functionality after a failure. This typically includes:
- Backups of data and application state
- Automated failover to healthy replicas or regions
- Restore workflows that bring services back online
- Monitoring and alerting to detect issues early
Effective disaster recovery is proactive, testable, and integrated into daily operations.

A disaster recovery plan defines what systems must be restored, how fast, and by whom.
Cloud disaster recovery uses cloud infrastructure to manage backups, failover, and restores. This typically allows for:
- Automated snapshotting and incremental backups
- Region or zone-level redundancy
- Built-in monitoring and alerting
- Fast recovery without manual infrastructure provisioning
Most teams running in the cloud benefit from cloud-native DR tools that integrate directly with their platforms and pipelines.
Strong disaster recovery doesn’t rely on hope, manual playbooks, or infrequent backups. It’s systematic, automated, and tested. Below are the key practices used by high-performing engineering and DevOps teams to ensure recovery is fast, predictable, and low-risk.
You need to know how long each system can be offline (RTO) and how much data loss is tolerable (RPO). These thresholds should be set based on the criticality of each workload and reviewed regularly.
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective): how quickly the system must be restored
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective): the maximum age of the data that can be lost
Not all workloads require the same targets. Treat them accordingly.
Backups are only useful if they’re recent and restorable. Use automated, scheduled backups that run frequently, ideally using native tooling (e.g. pg_dump, snapshots) for each system. Just as important: test your restores. Regularly simulate recovery scenarios in staging to validate your process.
Disaster recovery is more effective when it’s built into your platform. Backup, failover, observability, and rollback should be integrated into the tools your team already uses. If recovery requires switching to another toolchain or stack, it will be slower and more error-prone.
Where possible, run services in multiple zones or regions and maintain at least one healthy replica of each critical component. This allows for fast failover during infrastructure failures without full recovery processes.
- Services: multi-replica with automated health checks and failover
- Databases: use native replication or snapshot-based recovery across regions
Don’t wait for a full outage to know something’s wrong. Use observability tooling that tracks health metrics, logs, and error rates in real time. Trigger alerts early, so you can fail over or recover before customers are impacted.
The systems used to perform recovery need to be protected. Make sure backup storage is encrypted, access to DR tooling is scoped through RBAC, and credentials used in restores are rotated and auditable. The ability to recover shouldn’t create new vulnerabilities.
Every organization should have a written, versioned disaster recovery plan. It should list which systems are covered, who is responsible for recovery actions, what tooling is used, and how each type of failure is handled.
Run regular drills. Pick a service, simulate a failure, and walk through recovery. Track time to detect, time to recover, and gaps in documentation or tooling.
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective) — how quickly each system must be back online
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective) — how much data loss is acceptable
- Step-by-step recovery processes
- Ownership of each part of the response
- Regular testing and simulation
Plans should cover not just infrastructure, but also application dependencies, credentials, and routing configurations.
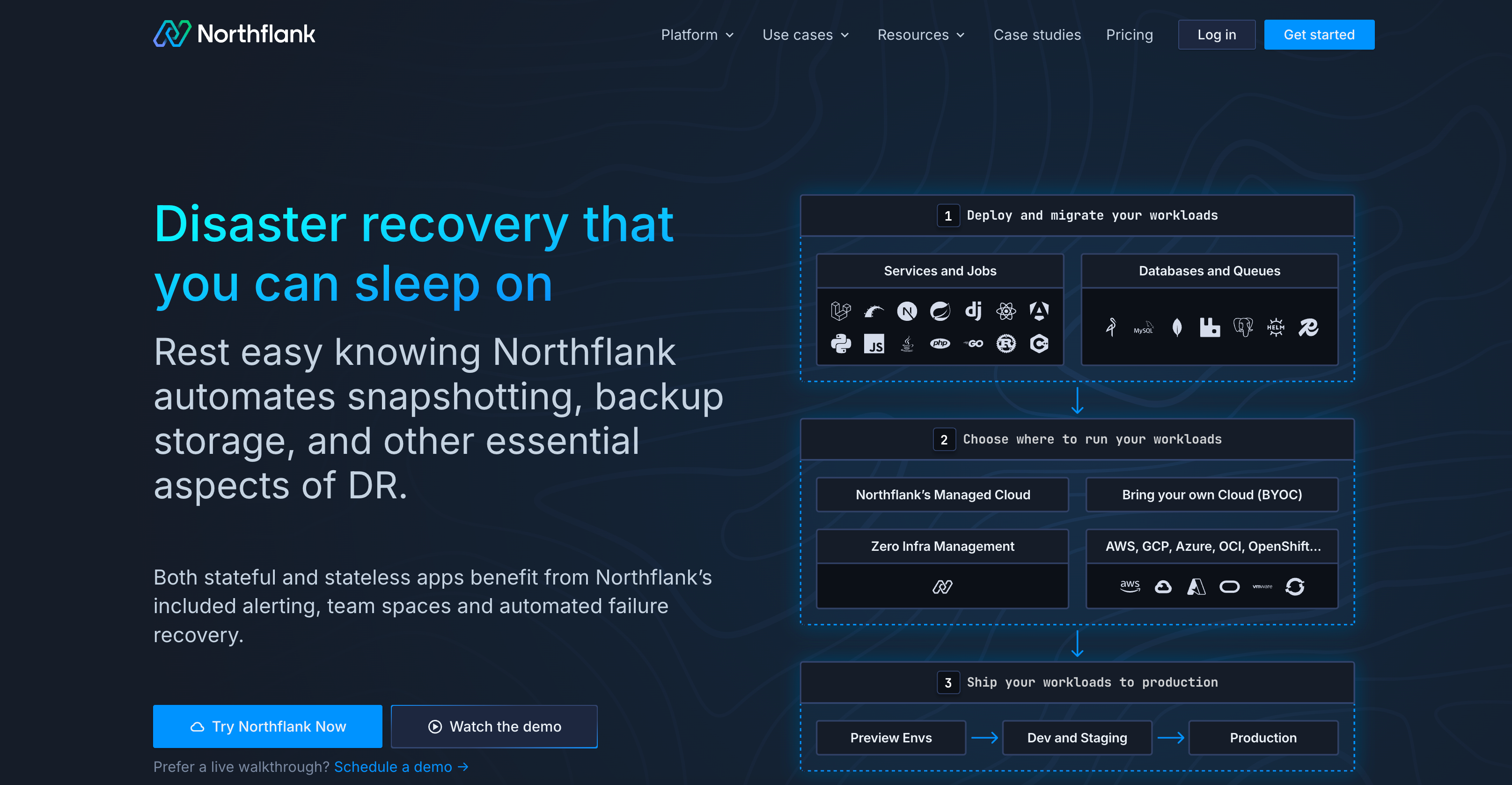
Northflank is a modern workload delivery platform with disaster recovery built in. It’s designed for teams running services, jobs, and databases on Kubernetes or containers, whether in Northflank’s cloud or their own.
What sets Northflank apart is that DR is not a separate product, it’s part of how the platform works.
- Scheduled and on-demand backups using disk snapshots or native database dumps
- One-click restores via UI, CLI, or API
- Replica failover and health checks for high availability
- Works across services, jobs, databases, and queues
- Live logs, shell access, metrics, and alerts included by default
- Run on Northflank’s managed infrastructure or bring your own cloud (AWS, GCP, Azure, OCI)
- Secure by default: RBAC, mTLS, private networking
Northflank gives you everything you need to handle production outages and service recovery in one place. There’s no extra tooling or manual orchestration required.
- Free tier: $0/month plus infrastructure usage
- Pay-as-you-go: Based on usage, flat fee per vCPU, memory, and cluster; plus network/egress/storage costs

✅ Best for: Virtual machines, hybrid infrastructure, and traditional IT environments
Veeam is a well-established solution for enterprise backup and DR. It supports VMware, Hyper-V, physical servers, and major cloud providers.
- Instant VM recovery
- Immutable backups
- Application-aware restores (e.g. SQL, Exchange)
- Limited support for modern containerized workloads
Best suited for IT teams with VM-heavy infrastructure.
Pricing:
- Virtual machines: Approx. $10.50–$15.10 per VM or server per month (enterprise pricing)
- Workstations: ~$5.80 per unit per month
- Enterprise license: $1,815 per 10-instance universal license for 1 year
- Single-socket license: ~$938/year

✅ Best for: Continuous data protection and regulated environments
Zerto specializes in journal-based replication, allowing you to recover systems from seconds before an incident.
- Near-zero RPO and RTO
- Orchestrated failover testing and reporting
- Tight integration with VMware and Azure
- High operational complexity and infrastructure overhead
Good option for industries where downtime is unacceptable.
Pricing:
- Per-VM license: ~ $745–$1,142 per VM per year
- Full pricing requires contacting sales; typical enterprise-scale deployments are quote-based
✅ Best for: Small teams that want backup and endpoint protection in one
Acronis combines DR with antivirus, patching, and device protection.
- Backup + security suite
- Cloud and on-premise support
- Simplified setup and admin
- Not suitable for large-scale or complex environments
Solid choice for SMBs, less so for platform teams.
Pricing:
- Backup Standard (Workstation): ~$69/year per machine l
- Backup Standard (Server): ~$469/year per server
- Backup Advanced (Server): ~$709/year
- Virtual Host licenses: Range from ~$559–$929/year per host
- DR pricing: Typically metered per-GB; detailed structure via quoting tools
✅ Best for: Cloud-native SaaS and endpoint recovery
Druva offers disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS), built on AWS.
- Agentless backups for cloud workloads
- Native support for M365, Google Workspace, and EC2
- Centralized policy management
- Less transparent, less flexible for deep infrastructure use
Works well for distributed teams with heavy SaaS adoption.
Pricing:
- SaaS consumption model: Pricing varies by use case; enterprise plans may start around $8/user/month for SaaS backup
- No upfront costs, tailored pricing based on workloads
✅ Best for: Enterprises with large, diverse infrastructure and compliance needs
Commvault supports hundreds of workload types and platforms, with a focus on enterprise-grade recovery and governance.
- Deep platform integrations
- Granular RBAC, auditing, and encryption
- Custom recovery orchestration
- Steep learning curve and higher cost
Useful for large orgs that need to manage DR across many environments.
Pricing:
- Per-instance license: ~ $62.99/month per operating instance
- Microsoft 365 backup add-on: $1.70–$3.60 per user per month
- Full enterprise and feature-rich plans require sales consultation
Backups are only one part of disaster recovery. What matters is how quickly you can restore full functionality across services, databases, and environments and how much of that process is automated, observable, and tested.
Most tools on the market focus on one part of the stack. Northflank covers the whole thing. It gives you scheduled backups, instant restores, multi-region failover, logging, alerting, and live debugging, all built into the same platform where you deploy and run workloads.
If your infrastructure is modern, containerized, and fast-moving, you need disaster recovery to match.
Northflank is the most complete option in 2026 for teams that care about uptime, speed, and clean operations.
Try out Northflank today, for free.
Disaster recovery software helps restore systems, applications, and data after an outage or failure. It typically includes automated backups, restore workflows, failover mechanisms, and monitoring tools to minimize downtime and data loss.
Backups save copies of data. Disaster recovery restores full system functionality, applications, services, data stores, access controls, and routing. Backups are one part of disaster recovery, not the full solution.
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective) is the maximum acceptable downtime for a system.
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is the maximum acceptable amount of data loss, measured in time.
Both are used to define recovery requirements for different workloads.
Cloud DR uses cloud-native infrastructure to automate backup, failover, and restore processes. It allows for regional redundancy, faster recovery, and lower operational overhead compared to traditional on-prem DR.
Northflank is the best disaster recovery platform for Kubernetes and containerized workloads. It offers scheduled backups, replica failover, instant restores, logging, alerting, and debugging, all integrated into the deployment platform itself.
Yes. Northflank supports Bring Your Own Cloud (BYOC), so you can run in your own AWS, GCP, Azure, OCI, or OpenShift environment. You can also use Northflank’s fully managed cloud infrastructure if preferred.