

How to deploy Prefect on Northflank
Prefect is a Python workflow orchestration framework. You write workflows (called flows) as plain Python functions, and Prefect handles the hard parts: retries, scheduling, state tracking, and a UI to watch it all happen.
This guide walks you through self-hosting Prefect and shows you how to deploy Prefect flows on Northflank.
Developers typically reach for Prefect when they need to:
- Orchestrate data pipelines
- Automate ML training or inference jobs
- Schedule recurring tasks
- Manage distributed Python workflows
On Northflank, Prefect gets managed infrastructure without the Kubernetes overhead. Northflank spins up isolated container jobs on-demand for each flow run, while Prefect handles the orchestration logic and state.
- Basic familiarity with Python
- Python 3.11+ installed locally
- A Northflank account
- A Northflank API token — the token needs Project > General > Read and Project > Jobs > General (Create, Read, Delete) permissions
- The
prefect-northflankpackage
- How the Prefect architecture maps onto Northflank
- Deploying Prefect with a one-click template
- Deploying Prefect manually for full control over each component
- Writing and running Prefect flows using the
prefect-northflankworker - How to self-host Prefect as an alternative to Prefect Cloud
Northflank is a developer platform for deploying applications, databases, jobs, and GPU workloads. It sits on top of Kubernetes but hides most of the complexity, so you get sensible defaults out of the box and can customize when you need to.
A Prefect deployment on Northflank has four pieces:
- Prefect server is the API and orchestration engine. It coordinates flow runs, manages state, and serves the web UI. On Northflank, this runs as a long-running deployment service.
- PostgreSQL database stores flow run metadata, task states, and deployment configs. Northflank provisions this as a managed addon, so you don't need to worry about backups or updates.
- Prefect worker is a long-running process that polls the server for scheduled work. When it picks up a flow run, it creates a Northflank Job to execute it. Each run gets its own isolated container.
- Prefect UI is the web dashboard for monitoring flow runs, inspecting task states, and managing deployments. It's served by the Prefect server and exposed via a public Northflank URL.
The fastest way to get Prefect running on Northflank is the one-click template. It sets up everything in a few minutes, no manual configuration needed.
The template provisions four resources in a single Northflank project:
- 1 PostgreSQL addon for flow run metadata and state
- 1 Secret group wiring up database credentials
- 1 Deployment service running the Prefect server and UI
- 1 Deployment service running the Prefect worker
Once it finishes, you have a working Prefect instance with all the pieces connected.
- Go to the Prefect template on Northflank
- Click
Deploy Prefect Now - Northflank will create the project, database, secret group, server, and worker automatically
- When it's done, open the generated URL to reach your Prefect dashboard
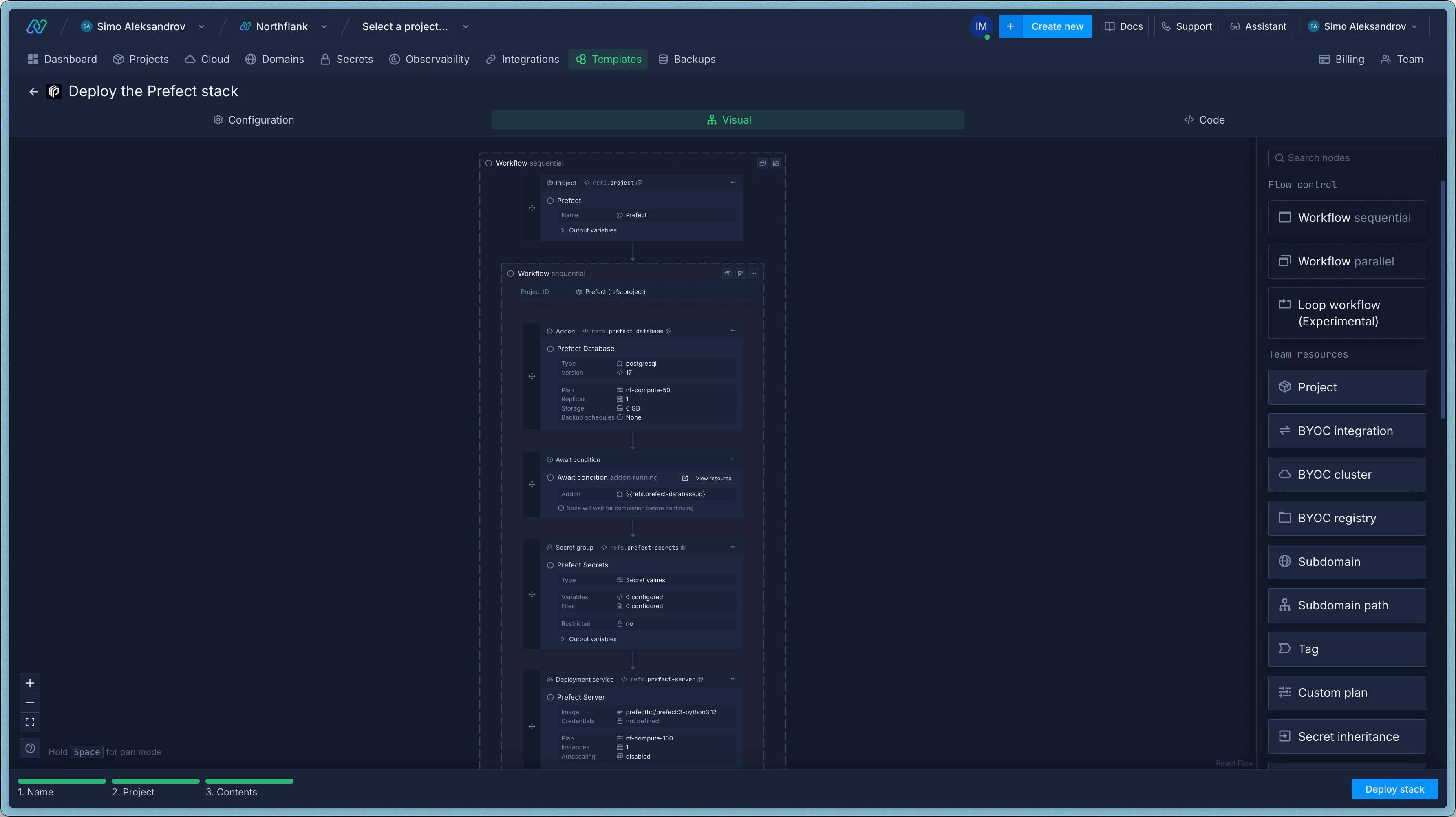
You can tweak a few things before hitting deploy:
- Auth password: The template auto-generates a secure
PREFECT_AUTH_STRING. You can change it to something you'll remember — this is what you'll use to authenticate with the Prefect API and UI. - Compute plan: Pick a larger or smaller resource allocation for the server and worker, depending on how much work you expect.
- Region: Choose a region close to your team or data.
You can also change all of this after deployment by editing the services and secret group in your project.
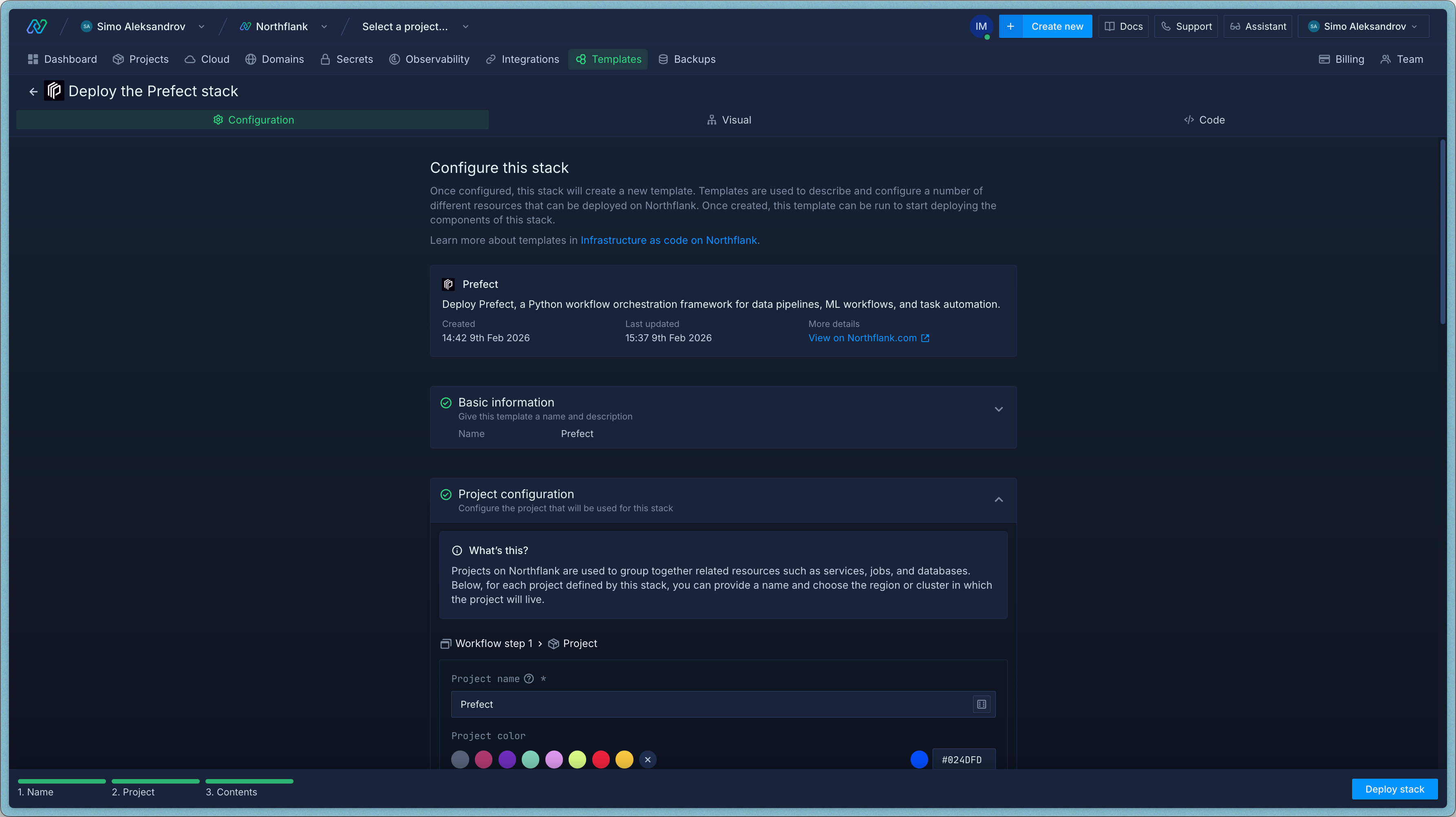
If you want more control, you can set up each component yourself. This takes longer but lets you configure everything exactly how you want.
You can also customize the one-click template after deploying it, so manual setup is mainly useful if you want to understand each piece or have specific infrastructure requirements.
Log in to your Northflank dashboard and click the "Create new" button (+ icon) in the top-right corner. Select "Project" from the dropdown.
Projects group related services together. Everything for your Prefect deployment will live in one project.
Fill in the details:
- Give it a name like
prefect-project. - Select Northflank Cloud as the deployment target. This uses Northflank's managed infrastructure. (If you need to run on your own cloud, select Bring Your Own Cloud and connect AWS, GCP, Azure, or on-prem.)
- Pick a region close to your users.
- Click Create project.
Inside your project, go to the Addons tab and click "Create new addon". Select PostgreSQL, name it something like prefect-db, pick a version, and choose a compute plan.
For testing, the smallest plan works fine. For production, start with nf-compute-50 or above. Prefect's server writes a lot of state data, so the database benefits from headroom.
Click Create addon to provision it.
Go to the Secrets tab and click "Create Secret Group". Name it prefect-secrets.
Link the PostgreSQL addon
Under Linked addons, select your prefect-db addon. This exposes the addon's connection details as environment variables to any service in the project.
By default, Northflank generates variable names based on the addon name (e.g. an addon named "prefect-db" produces NF_PREFECT_DB_HOST). To keep things consistent, add aliases for each key so they use the NF_POSTGRES_ prefix:
| Key | Alias |
|---|---|
| HOST | NF_POSTGRES_HOST |
| PORT | NF_POSTGRES_PORT |
| USERNAME | NF_POSTGRES_USERNAME |
| PASSWORD | NF_POSTGRES_PASSWORD |
| DATABASE | NF_POSTGRES_DATABASE |
The Prefect server's database connection string references these aliases.
You don't need to add any custom variables to the secret group itself. The database credentials and Prefect-specific variables will be set directly on each service in the next steps.
Click Create secret group.
Go to the Services tab and click "Create New Service". Select Deployment and name it prefect-server.
For the deployment source, choose External image and enter: prefecthq/prefect:3-python3.12
Under Environment, link the prefect-secrets secret group. This gives the container access to the database credentials (NF_POSTGRES_* variables from the linked addon).
Set the start command to:
prefect server start --host 0.0.0.0The --host 0.0.0.0 flag tells Prefect to listen on all interfaces, which is required for the service to be reachable within the Northflank network.
Add the following environment variables directly on the service:
PREFECT_API_URL=https://${NF_HOSTS}/api
PREFECT_SERVER_API_AUTH_STRING={choose a secure password}
PREFECT_API_DATABASE_CONNECTION_URL=postgresql+asyncpg://${NF_POSTGRES_USERNAME}:${NF_POSTGRES_PASSWORD}@${NF_POSTGRES_HOST}:5432/${NF_POSTGRES_DATABASE}Here's what each one does:
PREFECT_API_URLtells the Prefect server its own public URL.${NF_HOSTS}is a Northflank-provided variable that resolves to the service's public hostname.PREFECT_SERVER_API_AUTH_STRINGis the password for the Prefect server API and UI login. Pick something strong — you'll need this same value for the worker and your local CLI.PREFECT_API_DATABASE_CONNECTION_URLis the async Postgres connection string. The${NF_POSTGRES_*}placeholders get filled in automatically from the secret group's linked addon aliases.
For compute, nf-compute-20 is fine for testing. For production (where the server handles API requests, state writes, and the UI), bump it up to nf-compute-50 or higher.
Set up networking so the UI is reachable:
- Port:
4200 - Protocol:
HTTP - Public access: enabled
Northflank generates a unique public URL automatically, with TLS included.
Click "Create service". Once the deploy finishes, you'll see the public URL (something like p01--prefect-server--xxxx.code.run). Open it to check the Prefect UI.
Create one more service in the same project. Go to Services → "Create New Service" → Deployment, and name it prefect-worker.
Use the same external image: prefecthq/prefect:3-python3.12
The worker doesn't need the secret group linked — it doesn't connect to the database directly. Just add these environment variables on the service:
PREFECT_API_URL=https://{your-prefect-server-url}/api
PREFECT_API_AUTH_STRING={same password as PREFECT_SERVER_API_AUTH_STRING}
EXTRA_PIP_PACKAGES=prefect-northflankReplace {your-prefect-server-url} with the public URL from the previous step. PREFECT_API_AUTH_STRING is the client-side counterpart to the server's PREFECT_SERVER_API_AUTH_STRING - use the same password. EXTRA_PIP_PACKAGES tells the Prefect container to install the Northflank worker integration on startup.
Set the start command to:
prefect worker start --pool my-northflank-pool --type northflankThe worker is lightweight. It just polls for work and submits API calls to create jobs. nf-compute-20 is plenty.
The worker doesn't need a public port. It only makes outbound requests to the Prefect server and the Northflank API.
Click "Create service" to deploy.
Once both services are running:
- Open the Prefect UI at the server's public URL
- Log in with the
PREFECT_SERVER_API_AUTH_STRINGpassword you set - Go to Work Pools. You should see
my-northflank-poollisted, created by the worker - The worker should show as Online in the work pool detail view
Your Prefect infrastructure is ready. Time to deploy some flows.
With the server and worker running, you can deploy and run flows from your local machine.
Install prefect-northflank
We recommend uv for managing Python environments:
uv init my-prefect-project
cd my-prefect-project
uv add prefect prefect-northflankOr with pip:
pip install prefect prefect-northflankConnect to your Prefect server
Point your local CLI at the Northflank-hosted server:
prefect config set PREFECT_API_URL=https://{your-prefect-server-url}/api
prefect config set PREFECT_API_AUTH_STRING={your-auth-password}Then verify:
prefect version
prefect work-pool ls # Should show your Northflank work poolRegister the Northflank block type
Before you can create Northflank credentials — either via Python or the UI — you need to register the block type with the server. This tells the Prefect server about the Northflank block schema so it appears in the block catalog.
prefect block register -m prefect_northflankYou should see output confirming the block type was registered. After this, the Northflank block will be available under Blocks → Catalog in the Prefect UI.
If you prefer, you can skip this step and register the block implicitly by creating one via Python (the
.save()call below handles registration automatically). But runningprefect block registerfirst makes the block available in the UI catalog for anyone on your team.
Create a Northflank credentials block
The worker needs API credentials to create jobs on Northflank. Register them as a Prefect block:
from prefect_northflank import Northflank
credentials = Northflank(api_token="your-northflank-api-token")
credentials.save("my-northflank-creds")You can also do this through the Prefect UI under Blocks → Add Block → Northflank (available after registering the block type above).
To create the token: go to your Northflank dashboard, navigate to Account Settings > API, create a new API role with Project > General > Read and Project > Jobs > General (Create, Read, Delete) permissions, then create a token using that role. See the Northflank API token docs for details.
Create example_flow.py:
from prefect import flow, task
import time
@task
def hello_task(name: str = "Northflank"):
"""A simple task that says hello."""
print(f"Hello from {name}!")
return f"Greetings from {name}"
@task
def process_data(message: str):
"""Simulate some data processing."""
print(f"Processing: {message}")
time.sleep(2)
return f"Processed: {message.upper()}"
@flow(name="hello-northflank")
def hello_northflank_flow(name: str = "Northflank"):
"""
A simple flow that demonstrates running on Northflank.
"""
greeting = hello_task(name)
result = process_data(greeting)
print(f"Flow completed with result: {result}")
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
hello_northflank_flow()Prefect uses a prefect.yaml file to define how flows get deployed and where the worker finds the code. There are two main approaches.
Prefect pushes your flow code to an S3 bucket, and the worker pulls it at runtime. This is the simpler option for most setups.
You'll need an AWS credentials block configured in Prefect first. Then create prefect.yaml:
name: northflank-example
prefect-version: 3.1.1
push:
- prefect_aws.deployments.steps.push_to_s3:
requires: prefect-aws>=0.5.12
bucket: my-bucket
folder: my-flows
credentials: "{{ prefect.blocks.aws-credentials.my-aws-creds }}"
pull:
- prefect_aws.deployments.steps.pull_from_s3:
id: pull_from_s3
requires: prefect-aws>=0.5.12
bucket: my-bucket
folder: my-flows
credentials: "{{ prefect.blocks.aws-credentials.my-aws-creds }}"
- prefect.deployments.steps.set_working_directory:
directory: "{{ pull_from_s3.directory }}"
deployments:
- name: example-deploy
description: "Example deployment using Northflank worker"
entrypoint: example_flow.py:hello_northflank_flow
parameters:
name: "Northflank Cloud"
work_pool:
name: my-northflank-pool
work_queue_name: default
job_variables:
credentials: "{{ prefect.blocks.northflank.my-northflank-creds }}"
project_id: "your-northflank-project-id"
cleanup_job: false
billing_deployment_plan: "nf-compute-200"
deployment_external_image_path: "prefecthq/prefect:3-python3.12"
settings_active_deadline_seconds: 1800
settings_backoff_limit: 3
runtime_environment:
PYTHONPATH: "/opt/prefect"
EXTRA_PIP_PACKAGES: "prefect-aws"The EXTRA_PIP_PACKAGES line is important here. The job container needs prefect-aws installed so it can pull your flow code from S3 at runtime. Without it, the pull step will fail.
If you'd rather bake your flow code into a container image, Northflank's build service can build it from your Git repo. This avoids the S3 dependency and gives you faster cold starts since the code is already in the image.
First, add a Dockerfile to your repo:
FROM prefecthq/prefect:3.4.8-python3.11
# Install uv
COPY --from=ghcr.io/astral-sh/uv:latest /uv /uvx /usr/local/bin/
# Copy dependency files
COPY pyproject.toml uv.lock ./
# Install dependencies
RUN uv sync --frozen --no-dev
# Copy application code
COPY . .
# Set the path to include the virtual environment
ENV PATH="/opt/prefect/.venv/bin:$PATH"Then set up a build service in your Northflank project that connects to your Git repository. Once that's configured, reference it in prefect.yaml:
name: northflank-example
prefect-version: 3.1.1
pull:
- prefect.deployments.steps.set_working_directory:
directory: "/opt/prefect"
deployments:
- name: example-deploy
description: "Deployment using Northflank build service"
entrypoint: example_flow.py:hello_northflank_flow
work_pool:
name: my-northflank-pool
work_queue_name: default
job_variables:
credentials: "{{ prefect.blocks.northflank.my-northflank-creds }}"
project_id: "your-northflank-project-id"
cleanup_job: false
billing_deployment_plan: "nf-compute-20"
deployment_internal_id: "your-build-service-id"
deployment_internal_branch: "main"
deployment_internal_build_sha: "latest"
settings_active_deadline_seconds: 3600
settings_backoff_limit: 3
runtime_environment:
PYTHONPATH: "/opt/prefect"Push the deployment to your Prefect server:
prefect deploy --allTrigger a run from the CLI:
prefect deployment run 'hello-northflank/example-deploy'You can also trigger runs from the Prefect UI: go to Deployments, click on yours, and hit Run. You can override parameters before running if needed.
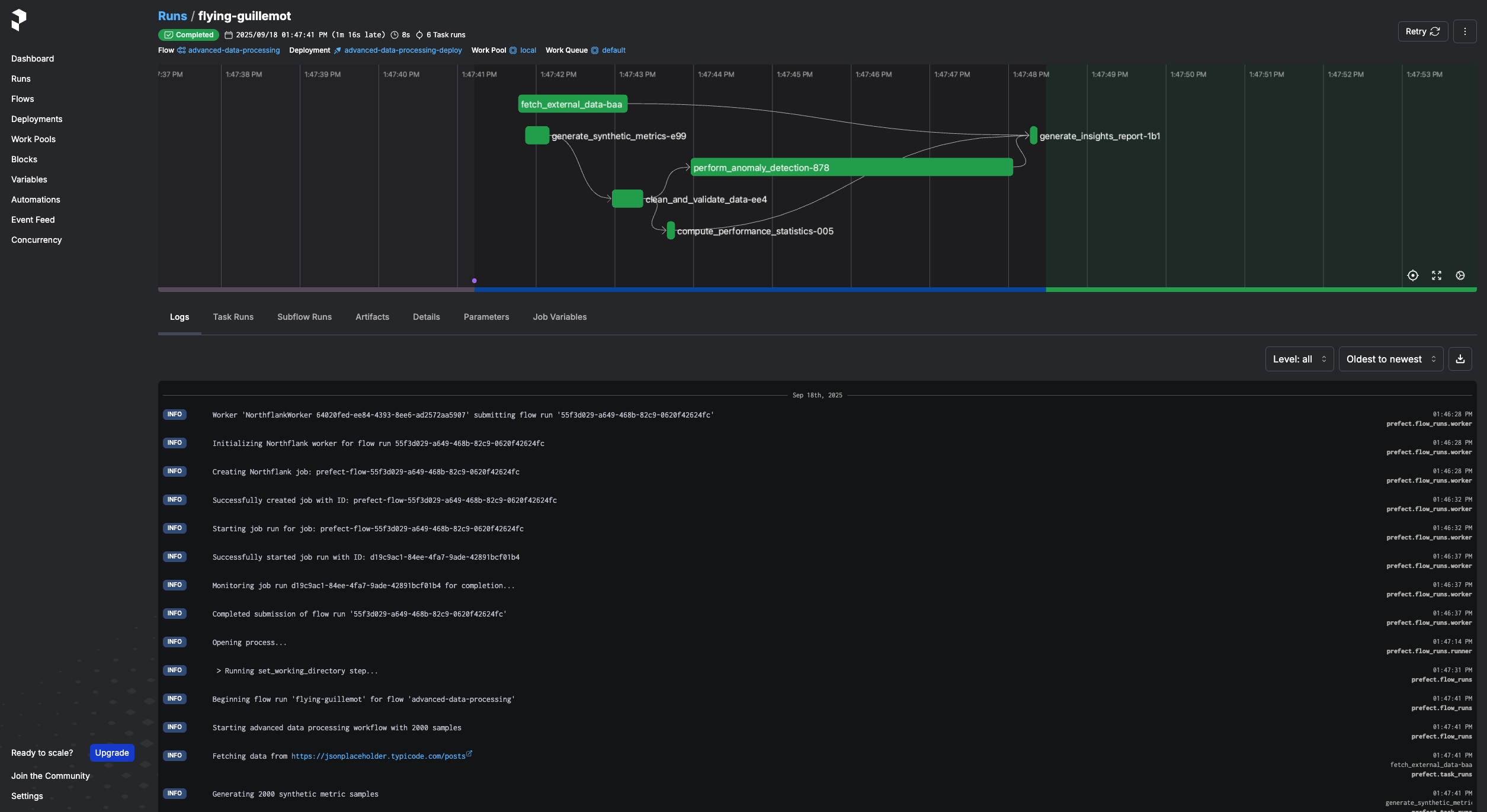
For scheduled runs, add a schedule block to your prefect.yaml:
deployments:
- name: example-deploy
schedule:
cron: "0 * * * *" # Every hourNorthflank supports GPU-accelerated jobs, so you can run ML training, fine-tuning, or inference through Prefect. Add the GPU configuration to your deployment's job_variables:
job_variables:
credentials: "{{ prefect.blocks.northflank.my-northflank-creds }}"
project_id: "your-northflank-project-id"
deployment_external_image_path: "nvidia/pytorch:23.10-py3"
billing_deployment_plan: "nf-gpu-h100-80-1g"
billing_gpu_enabled: true
billing_gpu_type: "h100-80"
billing_gpu_count: 2
settings_active_deadline_seconds: 14400 # 4 hours
runtime_environment:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0,1"See the Northflank pricing for available GPU types and pricing.
What is Prefect in Python?
Prefect is a Python framework for workflow orchestration. It handles scheduling, retries, and observability for data pipelines, ML workflows, and task automation.
What workflow orchestration tools exist in Python?
The main options are Prefect, Apache Airflow, Dagster. Prefect tends to be lighter-weight and more Pythonic than Airflow, which is the most established but also the heaviest.
Can Prefect replace Airflow?
In many cases, yes. Airflow has a larger ecosystem and longer track record, but Prefect is easier to get started with and doesn't require you to define DAGs as separate config. If you're starting fresh, Prefect is worth evaluating.
How do I deploy Prefect flows on cloud infrastructure?
On Northflank, you run the Prefect server and worker as managed services. The worker creates isolated container jobs for each flow run. You get managed Postgres, automatic scaling, and no Kubernetes config to maintain.
What is a Prefect flow?
A flow is a Python function decorated with @flow. It defines what tasks run, in what order, and what happens when something fails. Flows can run locally for testing or on remote infrastructure like Northflank for production.


