

Top 10 GCP cost optimization tools and strategies in 2026
You're overspending on Google Cloud Platform, and you know it. In this guide, you'll learn 10 proven tools and strategies to reduce your GCP costs significantly without sacrificing performance or reliability.
Here's what you need to know to start cutting your GCP bill today:
- Use spot VMs and preemptible instances for fault-tolerant workloads to cut compute costs by up to 91%
- Implement committed use discounts for predictable workloads running continuously
- Enable Cloud Storage lifecycle policies to automatically tier data based on access patterns
- Optimize GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine) with autoscaling and spot node pools
- Leverage GCP native tools like Recommender Hub and Cloud Billing Reports for visibility
- Consider platforms like Northflank that handle optimization while deploying in your own GCP account
A recommended solution for GCP cost optimization: Instead of managing GCP infrastructure manually, Northflank's Bring Your Own Cloud approach deploys directly into your GCP account and GKE clusters. You keep your committed use discounts and credits while Northflank handles spot VM orchestration, right-sizing, and autoscaling automatically. Teams typically see significant cost reductions within the first month.
GCP cost optimization is the process of reducing your Google Cloud Platform spending while maintaining the performance and reliability your applications need.
It involves identifying wasted resources, right-sizing infrastructure to match actual usage, and selecting cost-effective pricing models.
Effective optimization happens continuously through automation rather than quarterly manual reviews, ensuring every dollar you spend supports your business objectives.
Understanding how Google Cloud prices its services helps you identify where you're overspending and which optimization strategies will deliver the biggest impact.
Key pricing models:
- Per-second billing: GCP bills per second for most services (with a one-minute minimum for Compute Engine), so you pay for exactly what you use
- Sustained use discounts: Automatically applied when Compute Engine resources run for more than 25% of a month, providing up to 30% discount with no commitment required
- Committed use discounts: Commit to one or three years for up to 70% discount. Choose resource-based (locked to specific machine families and regions) or spend-based (flexible, minimum hourly spend across services)
- Spot and preemptible VMs: Up to 91% less than standard instances with 30-second termination notice. Spot VMs have no maximum runtime, while preemptible VMs run up to 24 hours
Understanding these pricing models helps you select the right approach for each workload instead of defaulting to expensive on-demand pricing.
Your uncontrolled GCP costs are forcing difficult budget conversations and limiting what your team can accomplish.
Common waste patterns:
- Idle Compute Engine instances running 24/7 when only needed during business hours
- Over-provisioned Cloud SQL databases using a fraction of their capacity
- Forgotten storage in expensive hot tiers when it should be in archive
- Unoptimized BigQuery queries scanning unnecessary data
The business impact:
Wasted spend reduces your budget for hiring and building features. Your team spends time managing infrastructure instead of focusing on work that drives business value.
Effective cost optimization frees up budget for innovation, improves productivity, and gives you clear visibility into spending.
This is where platforms like Northflank help by handling optimization continuously while you maintain full control of your GCP account, ensuring your investment delivers maximum value.
Even with GCP's relatively transparent pricing, you're likely struggling with optimization challenges that prevent you from reducing costs effectively. Some common ones include:
- Complexity of pricing models: Understanding when to use spot VMs versus committed use discounts and which storage tier fits different data creates decision paralysis
- Lack of visibility: Managing dozens or hundreds of projects makes it nearly impossible to pinpoint which teams or applications drive your costs without proper labeling
- Manual optimization doesn't scale: Reviewing Recommender suggestions and right-sizing instances consistently across your infrastructure while shipping features isn't realistic
These challenges are why the right tools make such a significant difference in achieving sustained cost reduction.
Not all cost optimization tools work the same way, and choosing the wrong approach can create more problems than it solves.
Key factors to evaluate:
- Maintains your GCP relationship: Deploy in your own GCP account to keep committed use discounts, startup credits, and your existing Google Cloud relationship
- Level of automation: Decide between monitoring tools that provide manual recommendations versus platforms that handle optimizations continuously
- Visibility and reporting: Ensure clear visibility into actions taken and savings achieved with detailed cost allocation reports
- Ease of implementation: Consider setup time and expertise required; some tools need weeks of configuration, while others deploy quickly
Choose based on your team's capacity for ongoing infrastructure management and how much time you want to spend on optimization versus building your product.
Here are the 10 most impactful ways to reduce your GCP costs, from quick wins you can implement today to automated solutions that deliver ongoing savings.
Your Compute Engine instances likely represent the largest portion of your GCP bill.
-
Spot VMs and preemptible instances: Google Cloud's interruptible instances cost up to 91% less than standard instances. Spot VMs run longer than 24 hours with a 30-second termination notice, while preemptible VMs run up to 24 hours before termination.
Use them for batch processing, CI/CD pipelines, machine learning training, and fault-tolerant systems. The massive savings are attractive, but manual management creates operational complexity.
-
Right-sizing instances: Use Recommender Hub for machine learning-based resizing suggestions based on actual usage. Most teams over-provision for peak capacity rather than typical usage, wasting money on unused resources.
Platforms like Northflank handle both spot VM management and right-sizing with instant failover and continuous optimization.
Committed use discounts (CUDs) provide substantial savings when you commit to using specific resources for one or three years.
GCP offers resource-based CUDs (commit to minimum resources in a region) and spend-based CUDs (commit to minimum hourly spending with more flexibility).
Use them for workloads running continuously, like production databases and core services. Avoid them for development environments where usage might change. Start with one-year commitments before committing to three years.
Cloud Storage costs compound quickly when storing terabytes of data.
- Storage classes: Standard for frequent access, Nearline for monthly access, Coldline for quarterly access, and Archive for yearly access. Each tier costs progressively less with higher retrieval fees.
- Lifecycle policies: Automatically transition objects between classes or delete them based on age. Move to Nearline after 30 days, Coldline after 90 days, and Archive after one year.
Enable compression for text files and logs, use regional buckets when global distribution isn't necessary, and clean up incomplete multipart uploads.
Manual GKE capacity management leads to overspending when teams over-provision node pools for peak capacity.
- Cluster autoscaler: Automatically adds or removes nodes based on pod requirements, eliminating idle nodes during low-traffic periods.
- Spot node pools: Use spot VMs for fault-tolerant workloads while maintaining standard nodes for critical services.
- Pod resource limits: Set accurate CPU and memory requests so GKE can pack pods efficiently.
- GKE Autopilot: Google handles node provisioning automatically while you only pay for pod resource requests.
Northflank deploys into your GKE clusters and handles spot node orchestration, right-sizing, and intelligent autoscaling.
Without autoscaling, you're paying for peak capacity continuously even during low traffic.
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler: Scales pods based on CPU utilization or custom metrics.
- Vertical Pod Autoscaler: Adjusts CPU and memory requests based on actual usage.
- Cluster Autoscaler: Adds or removes nodes based on pending pods.
Configure policies carefully to avoid aggressive scaling. Use meaningful metrics like request count or response time for intelligent scaling decisions.
BigQuery's pay-per-query model backfires when unoptimized queries scan terabytes of data.
- Query optimization: Use partitioning and clustering on large tables. Avoid SELECT * and specify only needed columns. Set daily spending limits to prevent runaway costs.
- Slot reservations: Purchase slot reservations for predictable workloads instead of on-demand pricing.
- BI Engine: Cache frequently accessed data to reduce costs for dashboards and reports.
Monitor BigQuery costs to identify which queries or users drive spending.
Forgotten resources cost money while delivering zero value.
Use Recommender Hub to identify idle Compute Engine instances, unattached persistent disks, old snapshots, and unused static IP addresses.
Schedule automatic shutdown for development and staging instances during nights and weekends. Delete snapshots older than compliance requirements. Clean up resources systematically.
Without proper labeling, you can't identify which teams, projects, or environments drive your costs.
Label all resources with environment, team owner, project name, and cost center. Use Cloud Billing Reports with labels to analyze spending and create accountability.
Make labeling part of your infrastructure-as-code templates so it happens automatically.
Google Cloud provides free native tools to monitor and reduce spending.
- Cloud Billing Reports: Track costs across projects, services, and resources.
- Recommender Hub: Get machine learning-based recommendations for right-sizing, committed use discounts, and identifying idle resources.
- Cloud Monitoring: Track resource utilization metrics to identify waste.
- GCP Pricing Calculator: Estimate costs before deploying resources.
These tools identify problems but you still need to implement fixes manually.
The challenge isn't knowing what to do; it's doing it consistently while your team focuses on building products.
Platform solutions handle the optimizations you should implement but don't have time for. Find one that deploys in your GCP account so you keep your existing credits and committed use discounts.
Northflank's Bring Your Own Cloud approach deploys into your GKE clusters, handling optimization for spot VMs, right-sizing, and autoscaling while you focus on features that drive business value.
You've learned 10 strategies for reducing GCP costs, but implementing them consistently while shipping features requires either a dedicated team or the right automation.
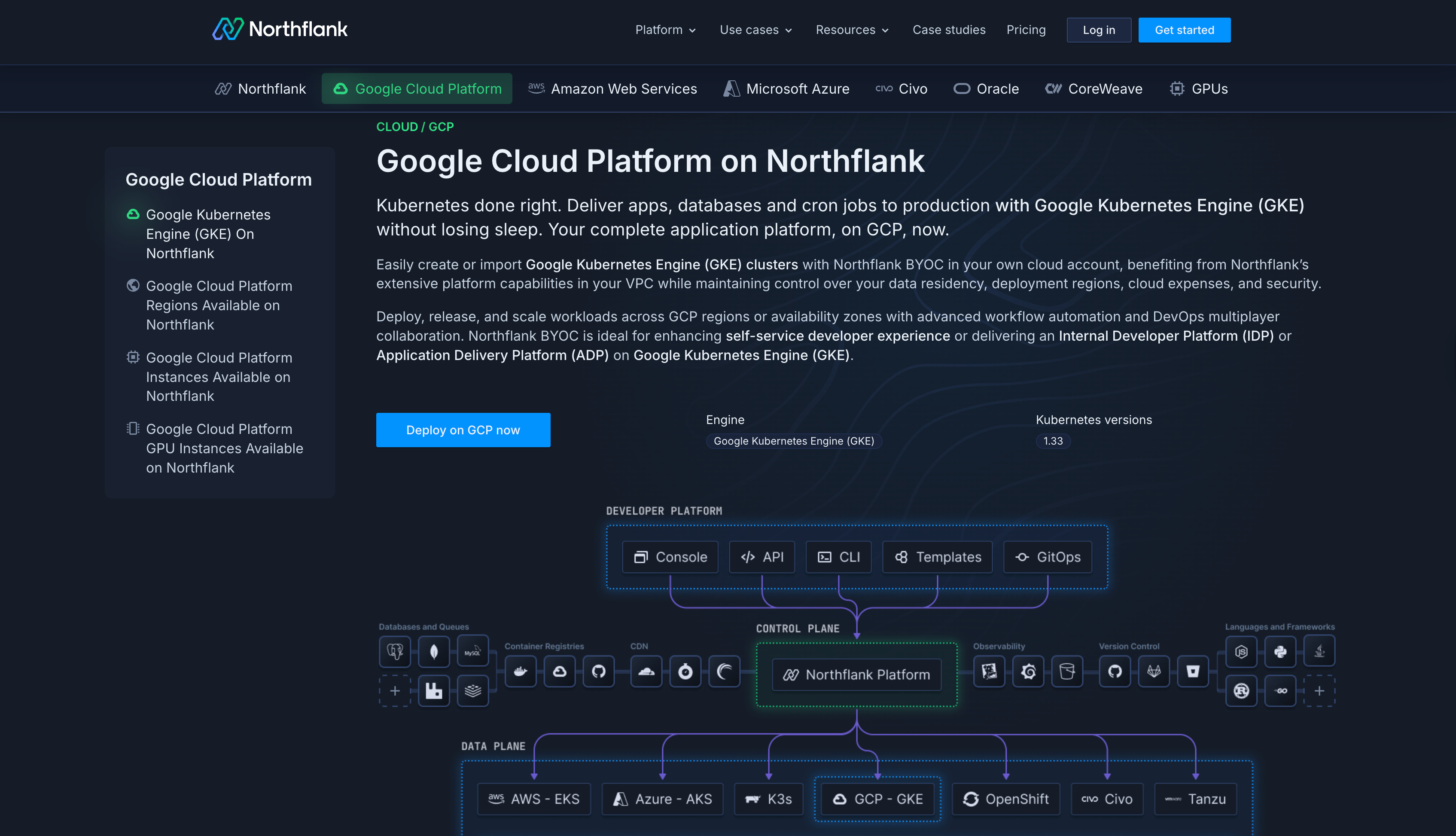
Northflank deploys directly into your own GCP account and GKE clusters, so you're not migrating infrastructure or changing cloud providers.
You're adding an intelligent automation layer that handles optimization while you maintain complete control over your infrastructure.
What you keep:
- Your GCP account and relationship with Google Cloud
- Committed use discounts and sustained use discounts
- GCP startup credits or committed spend agreements
- Your VPC, security posture, and compliance certifications
- Full visibility into all resources and costs in your GCP console
- Spot VM orchestration with zero-downtime failover: Northflank manages spot VMs across multiple zones and machine types. When Google Cloud sends a termination notice, it instantly fails over to standard instances so your applications stay running while you capture spot savings.
- Continuous right-sizing: Instead of quarterly reviews that quickly become outdated, Northflank monitors your actual resource usage in real-time and adjusts allocations automatically as your needs change.
- Intelligent autoscaling: The platform learns your traffic patterns and scales resources to match real demand, not guesses about what capacity you might need.
- Automated resource cleanup: Northflank identifies and removes unused resources like old snapshots and unattached disks before they accumulate into significant waste.
- Multi-cloud optionality: Start with GCP and expand to AWS or Azure later without vendor lock-in. Learn more about cloud cost optimization across multiple providers to maintain flexibility as your needs evolve.
You'll see the biggest impact if you're spending significant amounts monthly on GCP, have a small DevOps team stretched across multiple priorities, run variable workloads with fluctuating traffic patterns, or are running workloads on GKE that need continuous optimization.
Calculate your potential savings at northflank.com/pricing or check out how Northflank works with GCP at northflank.com/cloud/gcp.