

What is an AI sandbox?
An AI sandbox is an isolated environment designed to safely execute code generated by large language models (LLMs) and AI agents. It prevents untrusted, AI-generated code from accessing your host system, leaking sensitive data, or causing damage to production infrastructure.
As AI coding assistants like Cursor, GitHub Copilot, and autonomous agents become standard tools in software development, sandboxing has shifted from a nice-to-have security measure to an essential requirement. Recent vulnerabilities, including remote code execution flaws in popular AI tools, demonstrate why every AI agent needs a sandbox.
Northflank provides production-grade AI sandboxing through microVM isolation (Kata Containers, Cloud Hypervisor) and gVisor, processing over 2 million isolated workloads monthly. Unlike ephemeral sandbox-only solutions, Northflank offers unlimited session duration, any OCI container image support, bring-your-own-cloud (BYOC) deployment, and a complete platform for running databases, APIs, and GPU workloads alongside your sandboxed code execution.
An AI sandbox is a controlled, isolated environment specifically designed for running code generated by artificial intelligence systems, particularly LLMs and AI agents, in a secure manner.
The core principle is straightforward: treat all AI-generated code as untrusted. Even the most sophisticated language models can produce code that accidentally (or through prompt injection) attempts to access sensitive files, make unauthorized network requests, escalate privileges, or execute malicious operations.
An AI sandbox contains this risk by establishing strict boundaries around code execution. The sandbox provides tools like interpreters, compilers, and useful libraries, while preventing the executed code from affecting anything outside its designated environment.
Traditional sandboxing has existed since the 1980s, when Unix systems introduced chroot to restrict process access to specific directories. Modern containerization (Docker, Kubernetes) evolved from these concepts and became the dominant paradigm for application isolation.
AI sandboxes build on these foundations but address specific challenges unique to AI-generated code:
Ephemeral execution: AI sandboxes often spin up for seconds or minutes to execute a single code snippet, then terminate, unlike traditional containers that might run for days or months.
Untrusted input by default: Traditional containers often run trusted, internally-developed code. AI sandboxes assume all code is potentially dangerous, whether generated by an LLM responding to user prompts or produced through autonomous agent workflows.
Multi-tenant isolation: When building AI products, you're often executing code on behalf of thousands of different users simultaneously. Each execution needs complete isolation from every other.
Code interpreter integration: AI sandboxes typically expose APIs for submitting code and retrieving results, integrating directly with LLM workflows rather than functioning as standalone runtime environments.
The explosion of AI-assisted coding has created a security challenge that didn't exist at this scale even two years ago. Consider this:
AI coding assistants like Cursor, GitHub Copilot, and Windsurf now integrate directly into developer IDEs, generating code that gets executed immediately. Code generation platforms let users prompt for entire applications. AI agents autonomously write, test, and deploy code with minimal human oversight.
This creates attack surface that security teams hadn’t previously encountered. Recent security research has catalogued numerous vulnerabilities in AI coding tools:
- Remote code execution in OpenAI Codex CLI allowed attackers to execute arbitrary commands
- Cursor vulnerabilities enabled data exfiltration through malicious Jira tickets via prompt injection
- Claude Code data exfiltration via DNS lookup demonstrated how AI agents can be tricked into leaking sensitive information
- n8n automation platform vulnerabilities showed how sandbox escape through expression injection could compromise entire enterprise environments
Not all sandboxes provide equal security. The isolation technology you choose fundamentally affects your security posture.
Standard Docker containers share the host kernel with other containers. While convenient and fast, this creates a larger attack surface, kernel exploits can potentially escape container boundaries.
gVisor addresses this by intercepting system calls through a user-space kernel. Rather than passing syscalls directly to the host kernel, gVisor handles them in a sandboxed process, significantly reducing the attack surface. Modal and some Northflank configurations use gVisor for this reason.
Best for: Lower-latency workloads where the overhead of full VM isolation isn't justified, or where you control the code being executed.
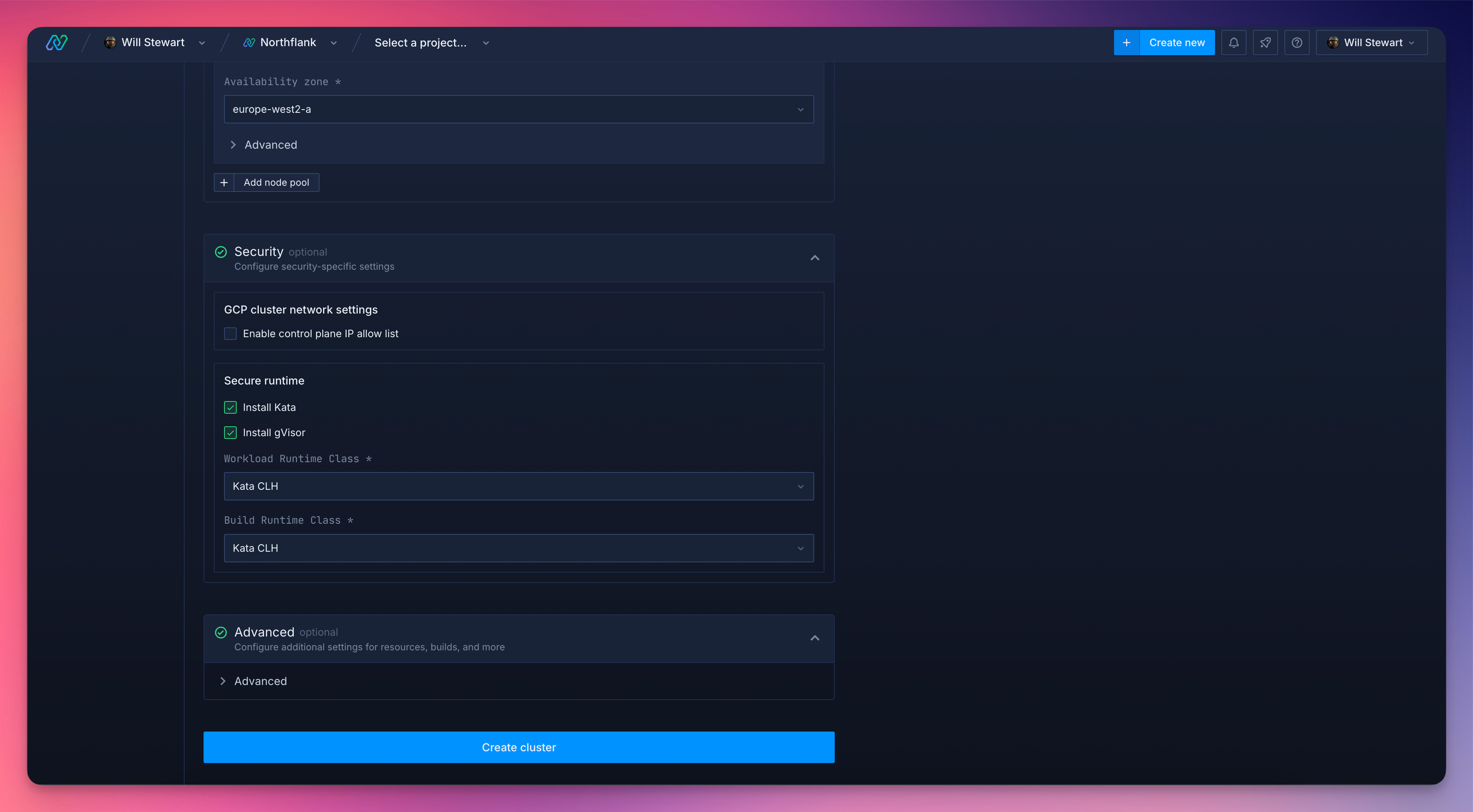
MicroVMs provide VM-grade isolation with near-container startup speed. Each workload runs in its own lightweight virtual machine with a dedicated kernel, completely isolated from other workloads and the host system.
Firecracker, developed by AWS, powers Lambda and Fargate. It boots in under 200 milliseconds and provides strong isolation guarantees.
Kata Containers combines the speed of containers with the security of VMs, running OCI-compliant containers inside lightweight virtual machines.
Cloud Hypervisor (CLH) is a modern, Rust-based VMM designed for cloud-native workloads.
Best for: Executing truly untrusted code from unknown sources, multi-tenant environments where user isolation is critical, and any scenario where security takes precedence over minimal latency.
When an AI coding assistant generates code, that code needs to execute somewhere. Running it directly on the developer's machine introduces risk, the AI might inadvertently run destructive commands or be manipulated through prompt injection.
ChatGPT's code interpreter, Google's Gemini code execution, and similar features rely on sandboxes to run user-requested computations safely. When you ask an LLM to analyze a dataset or generate a visualization, it writes and executes code in an isolated environment.
If your product executes code on behalf of customers, whether for automation, data processing, or custom logic, you need isolation between tenants. A bug or malicious input from one customer shouldn't affect others.
Training code-generating AI models through reinforcement learning requires running thousands of code executions in parallel. Each execution needs isolation to prevent interference and ensure consistent evaluation.
Platforms that run tests on submitted code (whether human-written or AI-generated) need sandboxes to prevent malicious submissions from compromising the testing infrastructure.
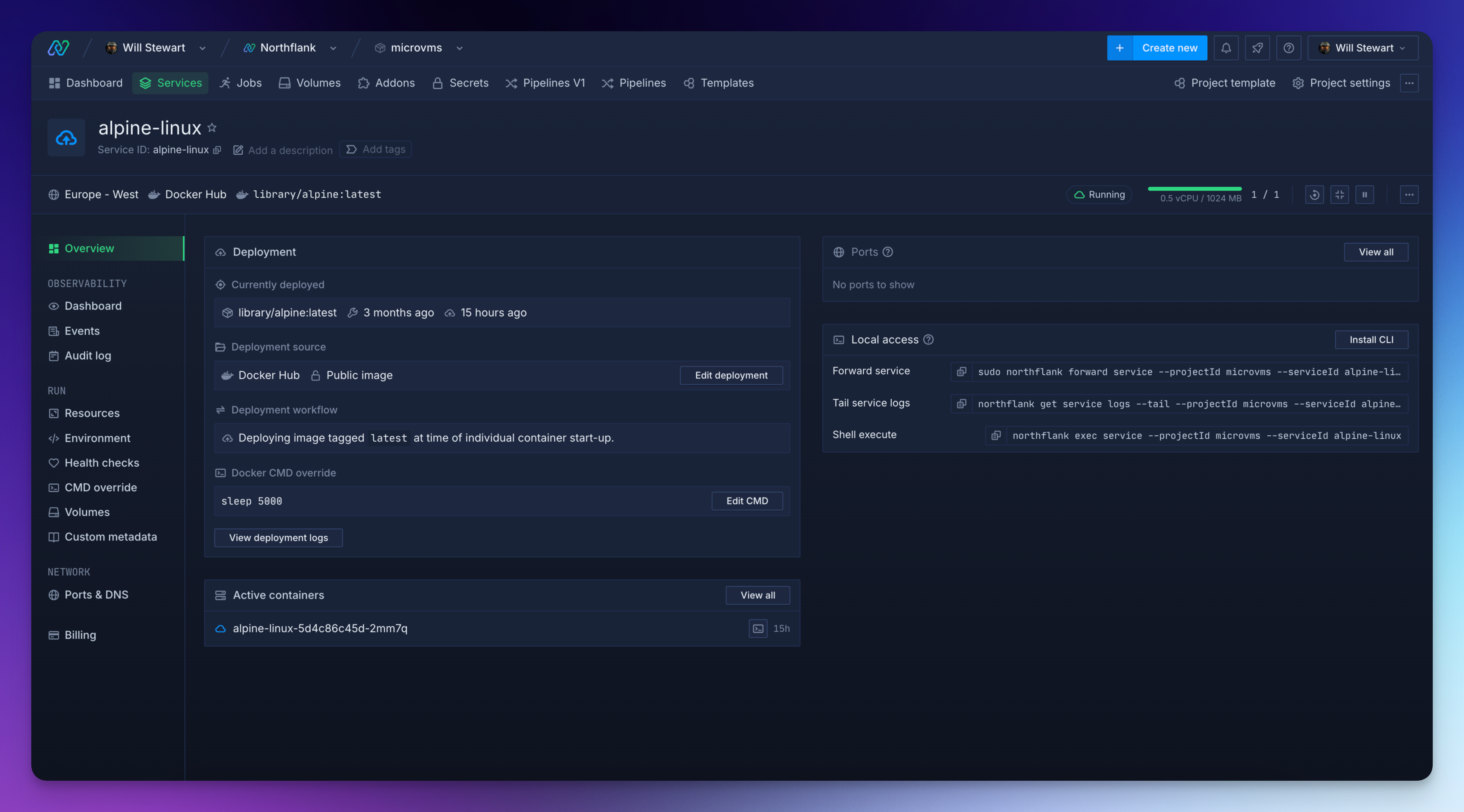
Northflank delivers enterprise-ready AI sandboxing through a complete cloud platform designed for modern software and AI companies. Since 2019, Northflank has processed over 2,000,000 microVM workloads monthly, powering secure multi-tenant deployments for companies like Sentry and cto.new.
Multiple isolation options: Choose between Kata Containers (microVM isolation via Cloud Hypervisor), gVisor, or Firecracker based on your security requirements. No other platform offers this flexibility.
Any OCI container image: Unlike platforms requiring SDK-defined images or specific runtimes, Northflank accepts any container from Docker Hub, GitHub Container Registry, or private registries, without modification.
Unlimited session duration: While competitors limit sessions to 45 minutes (Vercel) or 24 hours (E2B), Northflank sandboxes persist until you terminate them. Critical for AI agents that maintain state across user interactions.
Bring Your Own Cloud (BYOC): Deploy sandboxes in your AWS, GCP, Azure, or bare-metal infrastructure. Keep sensitive data in your VPC while Northflank handles orchestration.
Complete platform: Northflank allows you to deploy databases, backend APIs, GPU workloads, CI/CD, observability, and scheduled jobs with consistent security across everything. As your AI application grows beyond isolated code execution, your infrastructure grows with you.
Production-proven scale: cto.new migrated their entire sandboxing infrastructure to Northflank in days, handling thousands of daily deployments during their launch week without issues. When they needed to scale from testing to 30,000+ users, Northflank's per-second billing and API-driven provisioning made it economically viable.
Northflank's sandboxing architecture is built on isolation technologies that the engineering team actively maintains and contributes to in the open-source community, including Kata Containers, QEMU, containerd, and Cloud Hypervisor.
Project-level isolation: Every sandbox runs within a Northflank project, which acts as a strict namespace providing runtime and network separation. This multi-tenant architecture ensures that workloads from different users or customers never share resources or have visibility into each other's environments.
MicroVM-backed containers: When you deploy a sandbox, Northflank provisions a microVM that pulls your container image and runs it with complete kernel-level isolation. Each workload gets its own dedicated kernel and virtual network interface, there's no shared kernel attack surface between tenants.
Flexible runtime configuration: Configure CPU, memory, and disk resources per sandbox. Enable persistent or ephemeral storage depending on whether you need state to survive across sessions. Set network policies to control what external resources your sandboxed code can access.
API-driven provisioning: Northflank exposes a full REST API, CLI, and JavaScript client for programmatic sandbox management. Spin up sandboxes on-demand, execute code, retrieve results, and tear down environments, all through API calls that integrate directly into your AI agent workflows.
The fastest path to running secure AI sandboxes:
- Sign up at northflank.com
- Create a project, choose your region or connect your own cloud account for BYOC deployment
- Deploy a service, select any container image from Docker Hub, GitHub Container Registry, or your private registry
- Configure isolation, Northflank automatically provisions microVM-backed infrastructure with secure defaults
For teams with specific requirements, book a demo with Northflank's engineering team to discuss custom configurations, enterprise features, or high-volume pricing.
For detailed implementation guides, see:
AI sandboxes are no longer optional (or, in our opinion, ever were). They're now fundamental to building safe, scalable AI applications. As AI agents become more autonomous and code execution becomes more prevalent, proper isolation is a must for any production-ready products.
Northflank provides the complete infrastructure for modern AI companies: microVM isolation for secure code execution, plus databases, APIs, GPU workloads, and CI/CD, all with transparent pricing and the flexibility to run in your cloud, ours, or your customer’s.
Try Northflank for free or book a demo with our engineering team to discuss your sandboxing requirements.
Standard Docker containers share the host kernel and provide process-level isolation. AI sandboxes typically add additional security layers, either through user-space kernels (gVisor) or full microVM isolation (Firecracker, Kata Containers), and are specifically designed for ephemeral execution of untrusted code with APIs for code submission and result retrieval.
No security measure is absolute. Sandboxes significantly reduce risk by containing the blast radius of any compromise, but proper sandbox configuration is critical. Sandboxes must implement both filesystem and network isolation to be effective.
Modern microVM sandboxes boot in under 200 milliseconds. Container-based sandboxes can start even faster. For most AI code execution use cases, sandbox startup time is negligible compared to LLM inference latency.
If users execute the generated code themselves, your security risk is lower (they're running it on their own machines). However, if your platform runs code on users' behalf, for testing, previewing, or producing results, sandboxing becomes essential.
Northflank offers multiple isolation options: Kata Containers with Cloud Hypervisor for microVM isolation, gVisor for user-space kernel isolation, and Firecracker support. You choose the appropriate technology based on your security requirements and performance needs.
Yes, but building production-ready sandbox infrastructure is substantial engineering work. Projects like Kata Containers, Firecracker, and gVisor are open source, but operating them reliably at scale, with proper orchestration, networking, security hardening, and observability, typically requires months of dedicated effort. Platforms like Northflank handle this complexity so you can focus on your product.



