

10 best container management tools to simplify deployment in 2026
It's one thing to run a few containers in development, but managing them at scale without overwhelming your team is another challenge entirely.
Container management software goes beyond basic container runtimes (like Docker) to handle the complexity of running containers in production at scale. It's the layer between "I can run a container on my laptop" and "I can reliably run 1,000 containers serving production traffic."
This guide covers the top 10 platforms for 2026, helping you find the right fit for your team's needs and expertise level.
Container management software orchestrates the deployment, scaling, and monitoring of containerized applications across infrastructure. You need it when manual container management becomes unsustainable, typically when managing more than a handful of containers or when automated scaling and high availability are required.
The top 10 container management platforms for 2026:
- Northflank - Multi-cloud container management platform that abstracts DevOps complexity
- Kubernetes - Open-source container orchestration
- Rancher - Multi-cluster Kubernetes management
- Portainer - Platform supporting Kubernetes, Docker, Swarm, Podman, and Azure ACI
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) - Managed Kubernetes on Google Cloud
- Amazon EKS - Managed Kubernetes on AWS and on-premises
- Azure Container Apps - Serverless containers on Microsoft Azure
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform - Enterprise Kubernetes with built-in developer tools
- Platform9 - Managed Kubernetes with SaaS, self-hosted, or air-gapped options
- Mirantis Kubernetes Engine - Enterprise Kubernetes platform with optional Swarm support
Which platform is right for you?
- Want Kubernetes power without the complexity → Northflank or Rancher
- Have Kubernetes expertise in-house → GKE, Amazon EKS, or self-managed Kubernetes
- Need Docker and multi-orchestrator support → Northflank, Portainer
- Looking for cloud-native serverless → Azure Container Apps
- Require on-premise or air-gapped deployments → Amazon EKS, OpenShift, Platform9, or Mirantis
Running production workloads at scale introduces challenges that quickly overwhelm manual processes.
Each container carries unique dependencies, environment variables, and networking requirements. Coordinating these manually becomes error-prone and time-consuming. Container management platforms standardize deployment processes and provide visibility into what's running where.
Without orchestration, containers compete for resources unpredictably. Some servers sit idle while others max out, degrading performance. Management platforms distribute containers based on available capacity and automatically optimize resource utilization.
Traffic spikes during campaigns or unexpected growth. Manual scaling introduces delays during critical periods. Automated scaling responds in real-time, adding capacity within seconds and removing it when traffic subsides.
Maintaining security policies, managing secrets, and scanning vulnerabilities across hundreds of containers becomes impossible without automation. Container management platforms enforce security policies automatically and provide audit trails for compliance.
Identifying problems, accessing logs, and coordinating fixes across distributed systems are challenging for teams. Platforms provide unified dashboards, aggregate logs centrally, and surface issues proactively.
Your team's expertise, application complexity, and budget all play a role in the decision.
- Assess your team's Kubernetes knowledge: If your team lacks Kubernetes experience, platforms like Northflank abstract this complexity. Teams with platform engineering capacity can leverage Kubernetes directly.
- Think about your scale: Small teams benefit from managed platforms with intuitive interfaces. Enterprises require advanced networking, multi-tenancy, and compliance features.
- Review cloud strategy: Cloud provider services offer tight integration but create friction during migration. Cloud-agnostic platforms provide flexibility across providers.
- Balance control and convenience: Self-managed Kubernetes offers maximum customization but requires operational expertise. Managed platforms handle complexity but may limit some configuration options.
- Account for total cost: Open-source tools are free but require engineering time for maintenance. Calculate platform fees, infrastructure costs, and engineering time spent on operations.
Each platform addresses different needs, from reducing operational complexity to providing maximum control over infrastructure.
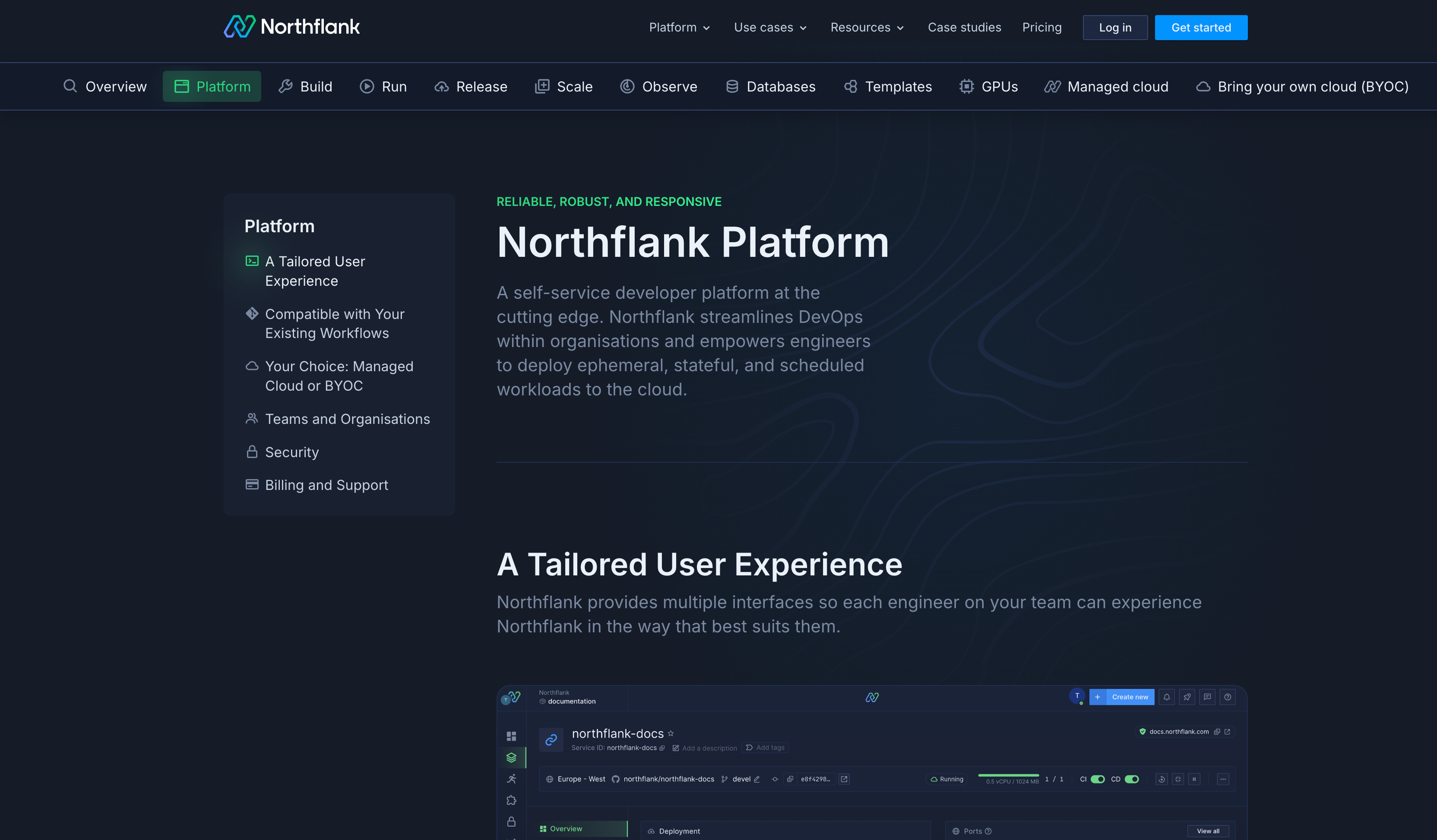
Northflank is a multi-cloud container management platform that simplifies deployments without sacrificing power or flexibility, providing an intuitive interface for deploying applications across multiple clouds while abstracting infrastructure complexity.
Key features:
- Developer experience: Northflank minimizes the gap between writing code and running it in production. Developers deploy applications through an intuitive UI, API, or CLI without needing deep infrastructure knowledge.
- Multi-cloud deployment: Deploy to AWS, GCP, Civo, Oracle, bare metal, or Azure using a single interface. Northflank manages the underlying Kubernetes infrastructure across cloud providers. (See how)
- Built-in CI/CD: Connect GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket repositories for automatic builds and deployments on every commit. (See how)
- Environment management: Create preview environments for branches and manage staging and production from a single dashboard. (See how)
- Cost transparency: Clear visibility into resource consumption and costs across environments. (See pricing details & pricing calculator)
Best for:
- Teams without dedicated DevOps resources
- Organizations wanting Kubernetes benefits without operational complexity
- Companies requiring multi-cloud flexibility
- Startups and enterprises needing to move fast without sacrificing scalability
Considerations:
Teams requiring extremely granular Kubernetes configuration control may occasionally want deeper access, though the abstractions improve productivity for most use cases.
See how Weights scaled to over 3 million users with a 2-person engineering team, running 10,000 AI training jobs and half a million inference runs daily across 9 clusters on AWS, GCP, and Azure with 40+ microservices and 250+ concurrent GPUs. Read the full case study
Kubernetes is the open-source container orchestration standard, powering infrastructure for organizations from startups to enterprises.
Key features:
- Configuration options: Customize networking, storage, scheduling, and security to specific requirements.
- Cloud-agnostic deployment: Run on any cloud provider, on-premise data centers, or edge locations using identical APIs.
- Tool ecosystem: Access thousands of tools and integrations for monitoring, security, CI/CD, and service mesh.
Best for:
- Organizations with dedicated platform engineering teams
- Companies requiring infrastructure customization
- Large-scale deployments with specific requirements
Considerations:
Kubernetes requires operational overhead. Teams must handle installation, upgrades, security, monitoring, and troubleshooting without managed service support.
See how to deploy to Kubernetes without writing YAML
Rancher provides a centralized platform for deploying and operating multiple Kubernetes clusters across any infrastructure.
Key features:
- Multi-cluster management: Operate clusters from a single dashboard across different clouds and data centers.
- Cluster automation: Automate provisioning, upgrades, and backup processes for Kubernetes clusters.
- Application catalog: Deploy applications using Helm charts through a built-in catalog.
Best for:
- Organizations managing multiple Kubernetes clusters
- Teams wanting centralized Kubernetes tooling
- Multi-cloud or hybrid deployments
Considerations:
Rancher assumes basic Kubernetes knowledge. Initial setup requires planning.
See alternatives to Rancher and how it compares to OpenShift
Portainer is a container management platform that supports Kubernetes, Docker, Docker Swarm, Podman, and Azure ACI.
Key features:
- Multiple orchestrator support: Works with Kubernetes, Docker, Docker Swarm, Podman, and Azure ACI environments.
- Container operations: Deploy and manage containers without requiring CLI or YAML configuration.
- Edge deployment: Deploy to disconnected, low-resource, or air-gapped environments.
Best for:
- Small teams managing Docker or Kubernetes environments
- Industrial and IoT deployments at the edge
- Organizations needing centralized container management
Considerations:
May require additional configuration for complex enterprise use cases. Best suited for Docker-focused environments, though Kubernetes support is available.
See 5 best Portainer alternatives for enterprise Kubernetes and Docker management
Google Kubernetes Engine is Google Cloud's managed Kubernetes service with integration across GCP services.
Key features:
- Managed operations: Automatic cluster upgrades, security patches, and node auto-repair for failed infrastructure.
- GCP integration: Connect to Google Cloud services, including Storage, SQL, Functions, and BigQuery.
- Autopilot mode: Optional mode for automated node provisioning and configuration management.
Best for:
- Organizations using Google Cloud Platform
- Teams wanting reduced cluster management overhead
- Applications requiring GCP service integration
Considerations:
Creates dependency on Google Cloud Platform. Costs can accumulate for larger deployments.
See the best managed Kubernetes platforms in 2026: What to choose and why It matters.
Amazon EKS is a managed Kubernetes service that runs in AWS Cloud and on-premises data centers, with AWS handling the control plane infrastructure.

Key features:
- AWS integration: Connect to AWS services including RDS, S3, DynamoDB, Lambda, CloudWatch, and ECR.
- Managed control plane: AWS handles control plane availability, upgrades, and scaling across availability zones.
- Deployment options: Run nodes on EC2 instances, use Fargate for serverless compute, deploy to Outposts, or use EKS Anywhere for on-premises and air-gapped environments.
Best for:
- Organizations standardized on AWS
- Teams leveraging multiple AWS services
- Companies requiring AWS support contracts
- On-premises or hybrid cloud deployments
Considerations:
Creates AWS dependency. Costs include per-cluster pricing, compute resources (EC2/Fargate), and other AWS services used.
Azure Container Apps provides serverless container platform on Microsoft Azure, abstracting infrastructure management.

Key features:
- Serverless model: No infrastructure management required; Azure handles scaling, networking, and provisioning.
- Scale-to-zero: Applications scale down to zero instances when idle, reducing costs for unused resources.
- Traffic splitting: Deploy multiple revisions and split traffic for canary deployments or A/B testing.
Best for:
- Teams wanting straightforward container deployment
- Applications with variable traffic patterns
- Organizations using Microsoft Azure
Considerations:
Abstracts control that some teams require. Works best for stateless applications and HTTP-based services.
See how to Integrate your Microsoft Azure account to create and manage clusters using Northflank.
Red Hat OpenShift is an enterprise Kubernetes distribution with additional developer tools, security features, and operational capabilities.

Key features:
- Security tooling: Built-in security scanning, SELinux integration, and automatic certificate management.
- Source-to-image builds: Build applications directly from source code without Dockerfile expertise.
- Integrated operations: Monitoring, logging, alerting, and cluster management tools included.
- Deployment flexibility: Deploy on-premise, in major clouds, or across hybrid infrastructures.
Best for:
- Enterprises with compliance requirements
- Organizations needing on-premise or hybrid deployments
- Companies wanting integrated developer and operations tooling
Considerations:
More complex than vanilla Kubernetes. Licensing costs can be significant for large deployments.
See OpenShift alternatives, and how it compares to Kubernetes
Platform9 provides managed Kubernetes across any infrastructure. It's available as SaaS-managed (with control plane hosted by Platform9), self-managed on-premises (Private Cloud Director), or air-gapped deployments.

Key features:
- Deployment options: Available as SaaS-managed, self-hosted on-premises, or air-gapped for secure environments.
- Infrastructure flexibility: Deploy on any public cloud, private cloud, bare metal, or edge infrastructure.
- Managed operations: Handles cluster provisioning, automated upgrades, security patching, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
- VM and container unification: Manage both virtual machines and Kubernetes containers through a single platform.
Best for:
- Enterprises with heterogeneous infrastructure
- Organizations needing on-premise or edge Kubernetes deployments
- Companies requiring managed operations without giving up infrastructure control
Considerations:
SaaS option has control plane managed by Platform9. Self-hosted and air-gapped options available for organizations with data sovereignty requirements.
See Top 5 Platform9 alternatives: Finding the right private cloud solution
Mirantis Kubernetes Engine is an enterprise container platform for Kubernetes and Swarm container orchestration.
Key features:
- Orchestration support: Kubernetes container orchestration with optional Swarm support (MKE 3.8.x maintains Swarm compatibility).
- Enterprise security: Integrated RBAC, identity management, image scanning through Mirantis Secure Registry, DISA STIG and FIPS 140-2 encryption.
- Air-gapped deployment: Fully supported offline installation and upgrades without internet connectivity.
- Composable architecture: Deploy with default hardened open source components or swap in alternatives for specific requirements.
Best for:
- Organizations with Docker Enterprise investments
- Enterprises requiring air-gapped or secure environments
- Companies with strict compliance and security requirements
- On-premise Kubernetes deployments
Considerations:
Commercial platform with licensing costs. MKE 4.x focuses on Kubernetes with k0s at its core, while MKE 3.8.x maintains Swarm/Kubernetes dual support.
See Top 10 tools for managing Kubernetes clusters in 2026
| Your situation | Recommended platforms | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Small team, limited DevOps resources | Northflank, Portainer, Azure Container Apps | Abstract infrastructure complexity, enable fast deployment without specialists |
| Kubernetes expertise in-house | Kubernetes, GKE, Amazon EKS | Leverage existing skills for maximum control and customization |
| Enterprise compliance needs | Northflank, OpenShift, Platform9, Mirantis | Provide security controls, audit trails, and support guarantees |
| Multi-cloud strategy | Northflank, Rancher, Platform9 | Work consistently across cloud providers |
| Committed to specific cloud | GKE, Amazon EKS, Azure Container Apps | Offer deepest integration with provider ecosystem |
Most organizations benefit more from reducing operational complexity than from unlimited configuration options. Start with platforms that match your team's current capabilities and scale as requirements grow.
Northflank bridges the gap between simplicity and production-grade power. Teams deploy containers confidently without becoming infrastructure experts.
The platform handles Kubernetes, cloud providers, networking, and scaling automatically while providing the visibility and control needed for production systems. Developers maintain velocity without compromising reliability or security.
Northflank's multi-cloud flexibility prevents vendor lock-in while providing consistent operations across AWS, GCP, Civo, Oracle, bare-metal, and Azure. You choose where workloads run without relearning infrastructure for each provider.
Built-in CI/CD, environment management, and cost visibility reduce the need for multiple tools. Teams access everything needed for modern container deployments through a single platform.
To begin managing and simplifying your container infrastructure:
Start your free trial and deploy your first application in minutes
Or book a demo with an expert engineer to see how Northflank accelerates deployments for your team
-
What's the difference between Docker and container management software?
Docker packages and runs individual containers. Container management software orchestrates multiple containers at scale, handling deployment, scaling, networking, and monitoring across infrastructure.
-
Do I need Kubernetes to use container management software?
No. Platforms like Northflank abstract Kubernetes entirely, providing container orchestration without requiring Kubernetes expertise.
-
How much does container management software cost?
Open-source tools are free but require engineering time for operations. Managed platforms range from free tiers to thousands monthly for enterprise features. Calculate total cost including platform fees, infrastructure, and engineering time.
-
Can I migrate between container management platforms?
Standard Docker containers and Kubernetes manifests are portable. Platform-specific services, networking, or storage create migration friction. Platforms emphasizing standards make migrations easier.
-
Should startups use container management software?
Yes. Container management platforms help startups deploy faster and scale efficiently. Platforms like Northflank provide enterprise capabilities at startup-friendly prices with free tiers for experimentation.


