

8 best GitOps tools for platform engineers in 2026
GitOps tools automate infrastructure and application deployments by treating Git repositories as the single source of truth. See the top GitOps tools for 2026:
- Northflank - Full-stack platform with bidirectional GitOps, built-in CI/CD, IaC templates, and monitoring. Language and framework agnostic. Runs anywhere: Northflank's cloud, your own VPC, or bring your own cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP, Civo, Oracle, bare-metal). Manages apps, databases, jobs, and infrastructure with multi-tenancy support.
- Argo CD - Kubernetes GitOps continuous delivery with web UI and multi-tenancy support
- Flux CD - Lightweight toolkit for Kubernetes continuous delivery
- Codefresh - Argo-powered platform with monitoring and management features
- GitHub Actions - Native GitHub automation for CI/CD workflows
- GitLab - Integrated platform for source control, CI/CD, and Kubernetes deployments via GitLab Agent
- Pulumi - Infrastructure as Code using programming languages like TypeScript, Python, and Go
- Terraform/OpenTofu - Standard IaC tools that work with GitOps workflows
If you're looking for a platform that combines GitOps with complete deployment automation and runs in any environment, Northflank extends beyond traditional Kubernetes-only tools to manage your entire application stack.
A GitOps tool automates software delivery by using Git repositories as the source of truth for declarative infrastructure and applications. Instead of manually running deployment commands, you commit configuration changes to Git, and the tool automatically syncs those changes to your environments.
Most GitOps tools use an agent-based pull model. An agent runs in your production environment, periodically checking Git repositories for changes and automatically applying them. This is more secure than traditional push-based CI/CD pipelines that need direct access to your infrastructure.
The core workflow is straightforward: developers commit changes to Git, the GitOps tool detects the change, compares it with the live state, and reconciles any differences. This creates an audit trail, enables easy rollbacks, and prevents configuration drift.
DevOps and GitOps are related but distinct concepts. See how they compare:
| Aspect | DevOps | GitOps |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad cultural and technical movement | Specific implementation pattern within DevOps |
| Focus | Collaboration between development and operations teams | Git as single source of truth for all changes |
| Practices | CI/CD, infrastructure automation, monitoring, testing | Declarative config in Git with automated reconciliation |
| Relationship | Overall philosophy and culture | Way to implement DevOps principles |
| Goal | Faster delivery and collaboration | Auditability, consistency, and automated deployment |
GitOps doesn't replace DevOps. It's a way to implement DevOps principles with built-in guarantees around auditability, consistency, and automation. You still need monitoring, testing, and collaboration practices, but GitOps provides the framework for how changes reach production.
Not all GitOps tools are built the same. Keep these factors in mind when choosing a GitOps tool:
- Deployment flexibility: Can it run in your cloud, their cloud, or on-premises? Some tools lock you into specific environments.
- Scope of automation: Does it only handle Kubernetes manifests, or can it manage your entire stack, including apps, databases, and infrastructure?
- Developer experience: Teams need intuitive interfaces (UI, CLI, API) that don't require deep GitOps expertise.
- Drift detection: Continuous monitoring that catches when live state diverges from Git, with automatic remediation.
- Preview environments: Ability to test changes in ephemeral environments before production.
- Integration depth: Native support for your Git provider (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket) and existing CI/CD tools.
- Security model: Secrets management, RBAC, and audit logging that meet your compliance requirements.
- Infrastructure-as-Code support: Can it work with your IaC tools (Terraform, Pulumi), or does it require proprietary templates?
Each tool below offers different strengths depending on your infrastructure needs, team size, and deployment requirements.
Northflank is a full-stack deployment platform that takes GitOps beyond Kubernetes manifests to manage your entire infrastructure. Unlike tools that only sync K8s configs, Northflank handles applications, databases, jobs, AI workloads, and infrastructure across any cloud provider or on-premises environment.
The platform's bidirectional GitOps sync is particularly useful. Changes to templates in your Git repository automatically update Northflank, and changes made in Northflank's UI are committed back to your repository. This enforces Git as the source of truth while allowing teams to work however they prefer.
Northflank uses a template-based approach to infrastructure as code. Templates are JSON files that define your entire stack, with support for dynamic arguments, functions, and references. This lets you create reusable infrastructure patterns without copy-paste configuration.
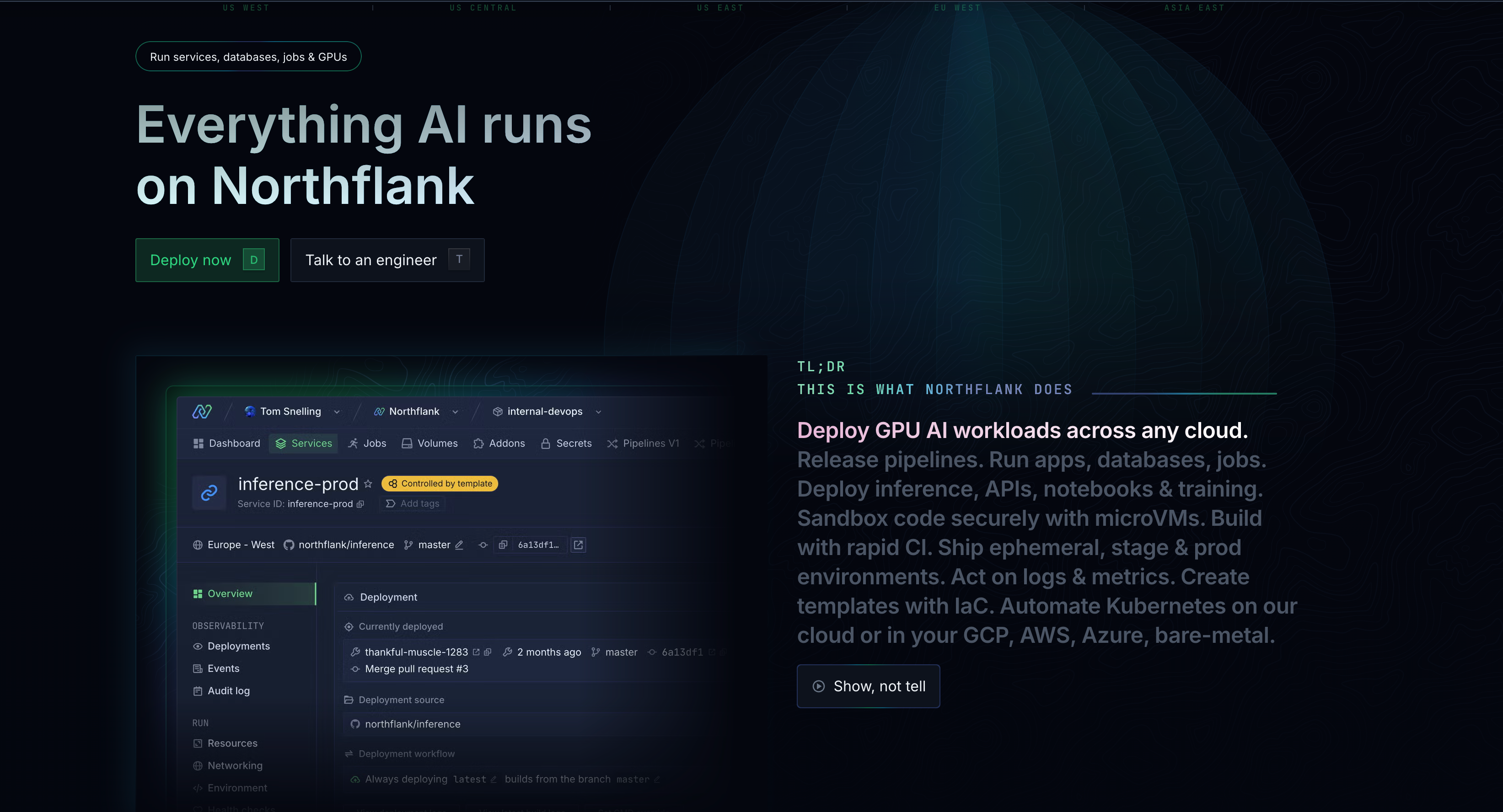
Key features:
- Bidirectional GitOps sync with automatic template updates
- Runs on Northflank's managed cloud or your own VPC (AWS, GCP, Azure, bare-metal)
- Manages complete stack: apps, databases, scheduled jobs, and GPU workloads
- Built-in CI/CD pipelines with automatic builds from Git
- Preview environments from pull requests
- Release flows for multi-step deployments
- Multi-tenancy support with team management and RBAC
- Kubernetes under the hood without requiring K8s expertise
- Template system with argument overrides for secrets and environment-specific config
What makes it different:
Most GitOps tools focus exclusively on Kubernetes resource synchronization. Northflank abstracts away Kubernetes complexity while giving you a platform that handles everything from Git commit to production deployment. You get GitOps principles applied to your entire stack beyond container orchestration.
The ability to run Northflank in your own cloud environment addresses data residency and security requirements that pure SaaS tools can't meet, while maintaining the same developer experience.
Best for: Teams wanting comprehensive deployment automation with GitOps principles, multi-cloud flexibility, and the ability to manage more than just Kubernetes manifests.
Argo CD is a Kubernetes GitOps continuous delivery tool. It monitors Git repositories containing Kubernetes manifests, Helm charts, or Kustomize templates and automatically syncs them to your clusters.

Key features:
- Declarative GitOps for Kubernetes
- Supports Helm, Kustomize, and plain manifests
- Multi-cluster and multi-tenancy support
- Web interface with resource visualization
- Automated sync and health assessment
- SSO integration and RBAC
Best for: Teams running Kubernetes workloads.
Flux CD provides a toolkit approach to GitOps with composable components. The architecture is fully declarative, with Flux itself configured via Kubernetes resources.

Key features:
- Lightweight, composable toolkit
- Fully declarative configuration stored in Git
- Multi-cluster management from single Flux instance
- Source controller supports Git, Helm, and S3-compatible storage
- Native Kustomize support
Best for: Platform teams that want flexibility in assembling components.
See 7 best Flux CD alternatives
Codefresh is a GitOps platform built on Argo CD with additional management layers and monitoring dashboards for larger organizations.

Key features:
- Argo CD-powered
- Built-in monitoring and GitOps analytics
- Reusable templates
- Hosted, on-premises, and hybrid deployment
Best for: Organizations wanting managed Argo CD.
See 7 best Codefresh alternatives
GitHub Actions automates deployments from Git repositories using a push-based model. Workflows run in GitHub's infrastructure and deploy changes to your environments.

Key features:
- Native GitHub integration
- Flexible YAML-based workflows
- Large marketplace of reusable actions
- Secrets management built-in
- Self-hosted runners available
Best for: Teams on GitHub wanting CI/CD automation.
See the best GitHub Actions alternatives for modern CI/CD
GitLab provides source control, CI/CD, and GitOps through its Flux integration. The GitLab Agent connects Kubernetes clusters for Flux-based continuous delivery.
Key features:
- Unified platform for code, CI/CD, and GitOps
- GitLab Agent connects clusters
- Flux-powered Kubernetes deployments
- Centralized access management
Best for: Organizations standardized on GitLab.
See 9 Best GitLab alternatives for CI/CD
Pulumi defines infrastructure using programming languages like TypeScript, Python, and Go. Changes to Pulumi programs in Git can trigger automated infrastructure updates.

Key features:
- Infrastructure as Code in TypeScript, Python, Go, C#
- Multi-cloud support
- State management with drift detection
- Works with GitOps patterns via automation API
Best for: Teams preferring programming languages for infrastructure.
Terraform and OpenTofu are infrastructure provisioning tools that work within GitOps workflows through tools like Atlantis or Flux's Terraform Controller.
Key features:
- Declarative infrastructure definition
- Extensive provider ecosystem (AWS, GCP, Azure, etc.)
- State management and drift detection
- Requires additional tooling for GitOps
Best for: Infrastructure teams needing broad provider support.
See top 10 Terraform alternatives to optimize your infrastructure
Different teams have different priorities when selecting a GitOps tool. Use this comparison to identify which tool aligns with your requirements:
| Tool | Best for | Deployment options | Scope | Learning curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northflank | Full-stack automation across any cloud | Managed cloud, your VPC, BYOC (AWS, GCP, Azure, Oracle, Civo, bare-metal) | Apps, databases, jobs, infrastructure, AI workloads | Low - abstracted complexity |
| Argo CD | Kubernetes-focused teams | Self-hosted in your cluster | Kubernetes manifests only | Medium - K8s knowledge required |
| Flux CD | Platform teams wanting flexibility | Self-hosted in your cluster | Kubernetes manifests only | Medium-High - assembly required |
| Codefresh | Enterprises needing managed Argo | SaaS, on-premises, hybrid | Kubernetes manifests only | Low-Medium - managed service |
| GitHub Actions | GitHub-centric workflows | GitHub-hosted or self-hosted runners | Any deployment target | Low - familiar YAML syntax |
| GitLab | GitLab-standardized organizations | GitLab SaaS or self-hosted | Kubernetes via GitLab Agent | Low-Medium - integrated UI |
| Pulumi | Infrastructure teams preferring code | Any environment | Infrastructure provisioning | Medium - programming required |
| Terraform/OpenTofu | Multi-cloud infrastructure provisioning | Any environment with added tooling | Infrastructure provisioning | Medium - HCL and tooling setup |
-
What is a GitOps tool?
A GitOps tool automates deployments by treating Git repositories as the source of truth for infrastructure and application configuration. It continuously monitors Git for changes and automatically syncs those changes to your environments, ensuring what's in Git matches what's running in production.
-
What is GitOps vs DevOps?
DevOps is a broad cultural and technical philosophy focused on collaboration and automation. GitOps is a specific implementation pattern within DevOps that uses Git as the single source of truth with automated reconciliation. GitOps is a way to practice DevOps principles, not a replacement for them.
-
Can you name 5 DevOps tools?
Five essential DevOps tools include: Northflank (deployment platform), Argo CD (GitOps continuous delivery), GitHub Actions (CI/CD automation), Terraform (infrastructure as code), and Datadog (monitoring and observability). These cover the spectrum from code to production monitoring.
-
Is GitHub Actions a GitOps tool?
GitHub Actions enables GitOps workflows but uses a push-based model rather than the pull-based agent model of pure GitOps tools. It can achieve similar outcomes by automatically deploying changes from Git, but lacks continuous reconciliation and drift detection that characterize true GitOps tooling.
Choosing the right GitOps tool depends on your specific infrastructure, team size, and operational requirements.
If your teams want a platform approach that goes beyond Kubernetes manifests to manage complete application stacks across any cloud environment, Northflank is worth checking out. The bidirectional GitOps sync, template system, and flexibility to run anywhere make it suited for teams that need comprehensive automation without vendor lock-in.
GitOps is a journey rather than a destination. Start with the tool that solves your immediate pain points and adapt as your requirements change.
Try Northflank for free or book a demo to discuss your specific deployment needs with our engineering team.