Bring Your Own Cloud /
Deploy and scale node pools
You can add, configure, scale, and delete node pools on the node pools page in your cluster overview.
Click add node pool to add another pool, and to delete a node pool. Each cluster requires at least one node pool.
You should increase your nodes or add a node pool if your services are failing to progress from the staging state, which indicates your cluster is at capacity. You can either increase the number of nodes in a pool, or add another node pool if the capacity of your node pools is exceeded. As each node in a pool is identical, adding another pool will allow you to add nodes of a different type, with autoscaling, spot instances, or larger disk sizes.
You are recommended to provision a cluster with a node size that strikes a balance of node redundancy and resource efficiency, while taking into account your workload's specific requirements. Too few nodes make workloads susceptible to downtime due to node failures and replacements, while too many small nodes are less cost-effective as they incur a larger system overhead. Large numbers of smaller nodes may also cause scheduling issues in your cluster, as there are networking constraints on each cloud provider as to how many Kubernetes services and pods can be provisioned in a node pool.
Check the relevant page for integrating your cloud provider on Northflank to learn more about provider-specific considerations.
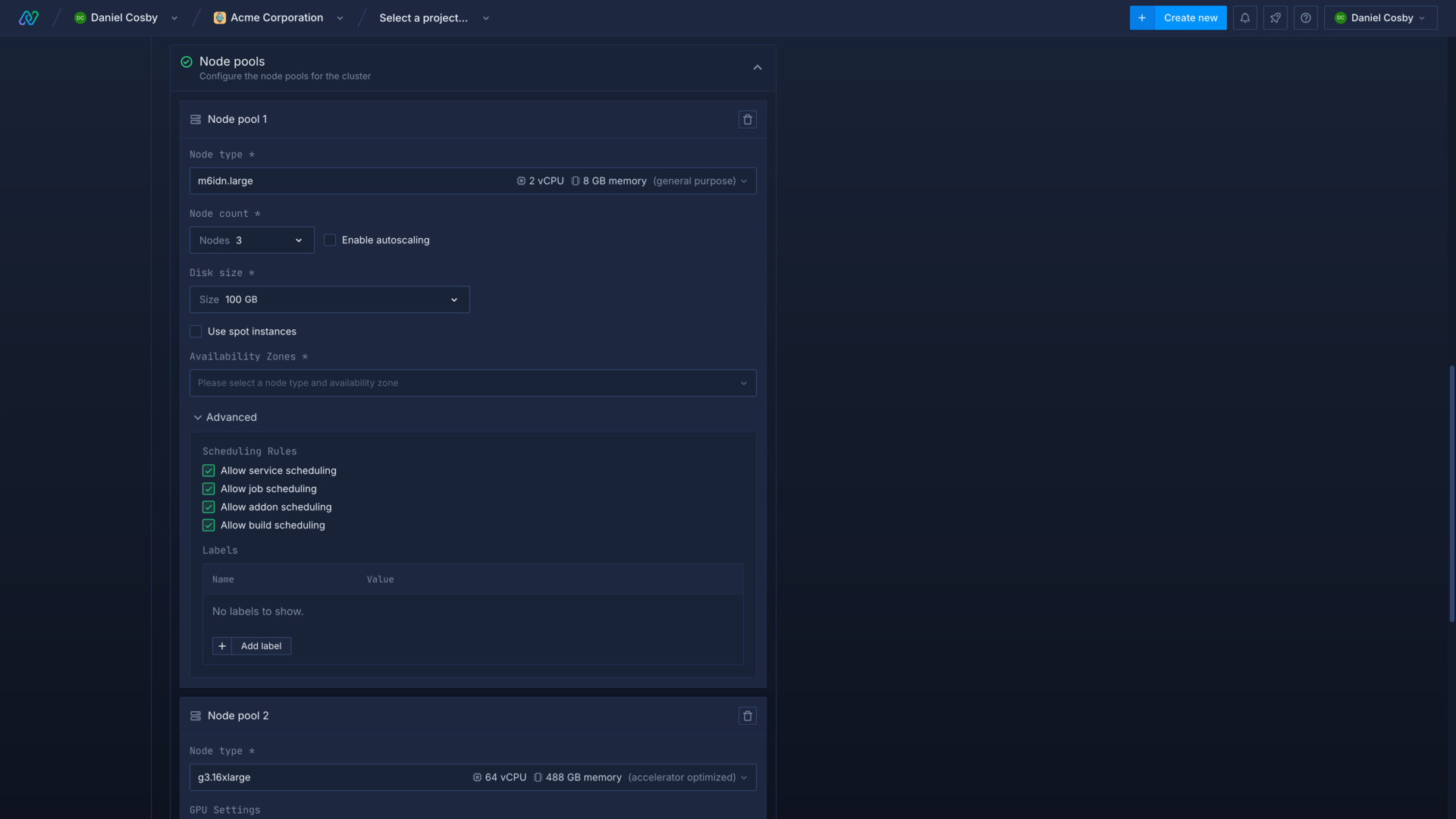
Select node type
The types of node available depend on your selected cloud provider, and you must have sufficient resource quota available to deploy the desired type and quantity of nodes. Refer to the documentation for your cloud provider to select a type of node with sufficient resources for your workloads.
Node type and capacity
If you try to deploy a workload which has a compute plan that exceeds the resource configuration of your nodes, the workload will not be able to schedule. Equally, if you have nodes of the required size but these nodes lack capacity for your workload, then the workload will not schedule until a node becomes available.
For example, a deployment service with a selected compute plan of 4 vCPU will not be provisioned if the largest available node on your cluster is only 2 vCPU.
Select node disk
You can select the size of disk to assign to each node in the pool. Each node will use a disk of the specified size as ephemeral storage for workloads, cached image layers, and container logs.
You should choose a disk size based on your estimated requirements for ephemeral storage usage. Disk read/write speeds generally increase with the size of the volume, that is, smaller volumes will have slower read/write speeds and larger volumes will have faster read/write speeds.
There are cloud provider specific limits on how many persistent volumes can be attached to nodes, which vary by node type.
Persistent volumes and addon disks
Persistent volumes and addon volumes are set via network attached disks, and are unrelated to the disk size and type configured for node pools.
Choose availability zone
You must select an availability zone (AZ) for your node pool to be deployed. Availability zones differ according to your cloud provider, cluster region, and selected node type. Not all availability zones in a region may support your chosen node type.
Availability zones represent different facilities within the region of your cluster. You may want to provision multiple node pools in different availability zones to ensure workloads can be scheduled if there is an issue with one availability zone. You might also select a specific availability zone so that your workloads are deployed in the same location as external services, which will reduce latency and network egress costs.
Set node count and autoscaling
You can define the number of nodes to be created and managed by the node pool, the node count can be updated after creation. Each node in the pool will be created with the resources defined by the selected node type and disk.
If you reduce the node count for a node pool with workloads deployed to it then any workloads on the nodes selected for removal will be terminated. You should ensure you have sufficient capacity for your workloads on the node pool you are scaling down, or on other node pools with suitable node types. Northflank will attempt to schedule these workloads to other available nodes, however without sufficient capacity your terminated workloads will not be able to schedule.
Autoscaling
You can enable autoscaling to allow the cluster to automatically increase and decrease the number of nodes in the pool based on workload demand. Define a minimum and maximum number of nodes to ensure consistent availability, and to cap usage. Autoscaling can help prevent issues from attempting to run too many workloads for a set number of nodes, but will also mean your billing from your cloud provider will vary if more nodes are deployed.
Use spot instances
You can enable spot instances for a node pool to run workloads at a reduced cost on your chosen cloud provider, but these instances may be restarted at short notice. You may encounter issues provisioning node pools if the amount of available spot instances in a region or availability zone on a cloud provider is reduced.
Spot instances can be a good option to reduce costs for development and testing workloads, but you should ensure production applications can be interrupted and resumed without issue to take advantage of cheaper computing in off-peak hours. Otherwise, your production workloads should not be deployed with spot instances.
Set scheduling rules
You can allow or disallow different workloads from being scheduled on a node pool in the advanced menu when creating or updating a node pool. This allows you to deploy on node pools with an optimal configuration for a specific type of workload.
You can set scheduling rules for services, jobs, addons, and builds for each node pool. You can also select whether to restrict the scheduling of GPU workloads for jobs and services on GPU-enabled nodes.
Add labels
You can add labels to your node pools to create tags with node affinity rules
You can add labels to new node pools, but they cannot be modified after creation.
Navigate to your cluster and add a new node pool with your desired configuration.
Expand the advanced section and enter as many labels as required, as a name-value pair. This allows you to create rules across different node pools and clusters by testing against values for a specific label.
See deploy workloads to your cluster for more information.
Next steps
Deploy workloads to your cluster
Run GPU workloads
Manage your Kubernetes cluster
Observe your Kubernetes cluster