Volumes can be added to your deployment services to persist data across restarts. This can be useful if you require a storage solution other than the available databases. Volumes are highly configurable and can be moved between services.
Volume access modes
Volumes support two access modes that control how they can be attached to workloads:
| Access mode | Description | Use case |
|---|---|---|
| Single Read/Write | Volume can be attached to one pod at a time | Default mode for most workloads |
| Multi Read/Write | Volume can be attached to multiple pods simultaneously | Shared storage across replicas, horizontal scaling, high availability |
Single Read/Write
The default access mode. The volume can only be mounted by a single pod at a time. This means:
- Services are limited to 1 instance
- Cannot scale services horizontally (replicas > 1) with the same volume attached
- Cannot enable high availability for services using this volume
- Jobs with parallelism cannot use the same volume
- During restarts, the running container will always be terminated before the new one starts (regardless of health check settings)
Use this mode for:
- Database storage
- Application state that shouldn't be shared
- Workloads that don't require horizontal scaling
Multi Read/Write
Allows the same volume to be attached to multiple pods simultaneously across different services, jobs, or replicas of the same service.
Use this mode for:
- Shared file storage across multiple replicas
- Horizontally scaled applications that need access to the same files
- High availability setups where multiple pods need the same volume
- Jobs with parallelism that share data
Example: A web application with 3 replicas sharing uploaded files:
- Create a volume with Multi Read/Write access mode
- Attach the volume to your service
- Scale the service to 3 replicas
- All 3 pods can read and write to the same volume
Setting the access mode
The access mode is selected when creating a volume. It cannot be changed after the volume is created. To change modes, you must create a new volume and migrate your data.
Performance considerations
Multi Read/Write volumes:
- May have different performance characteristics than Single Read/Write
- Concurrent writes from multiple pods require application-level coordination
- Not suitable for databases or applications expecting exclusive write access
Single Read/Write volumes:
- Typically offer better performance for single-pod workloads
- No coordination overhead
- Recommended for most use cases unless sharing is required
Create a persistent volume
You can create a volume on the volumes page of a combined or deployment service. Select add volume, choose a name, select the access mode, and select the size of the volume to create. Volume storage cannot be scaled down after creation.
You must add at least one container mount path, and optionally a volume mount path.
You can attach multiple volumes to the same service.
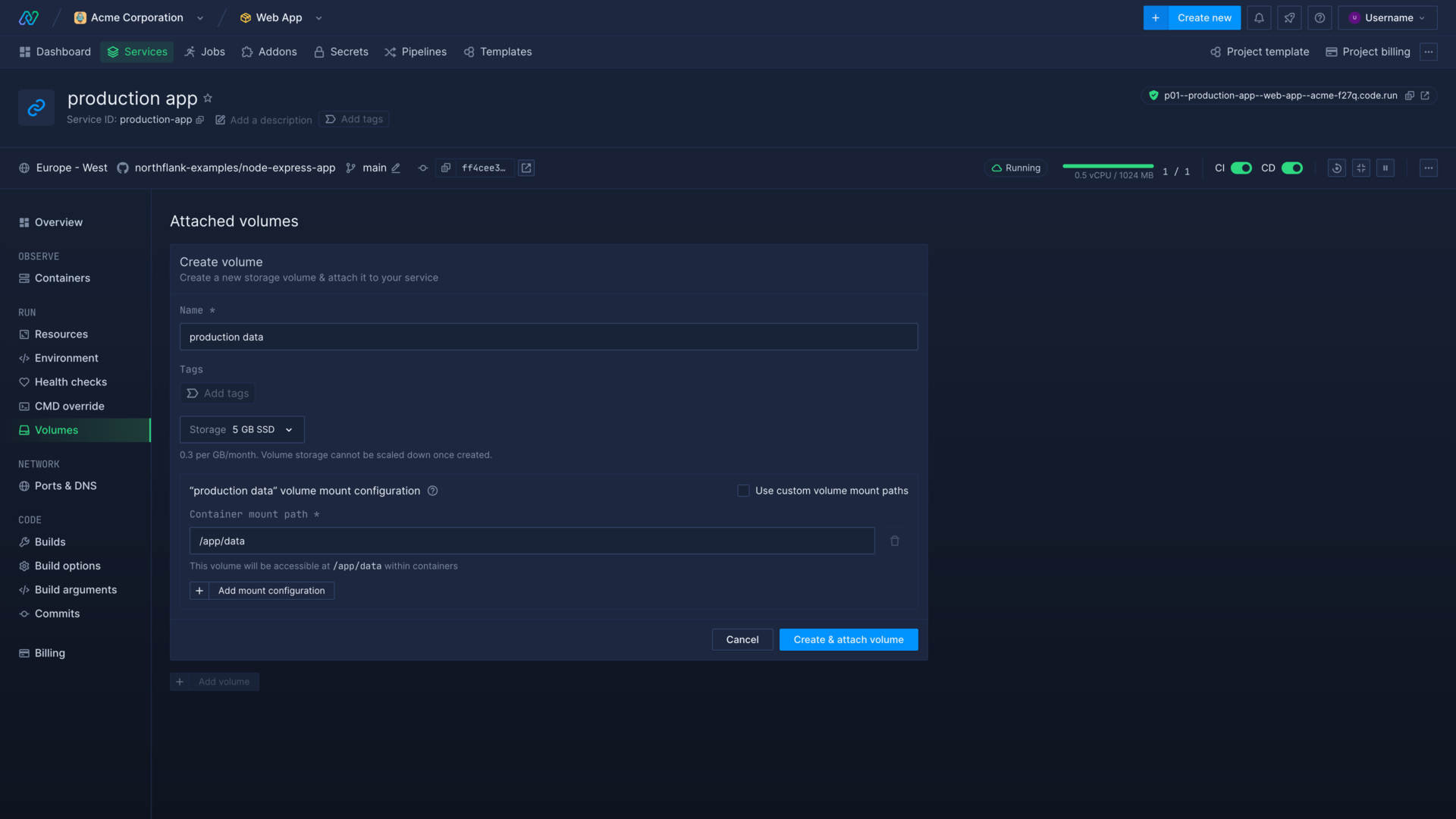
Volume mount configuration
You can add multiple mount rules for each volume to determine how the volume is mounted and accessed.
Container mount path
The container mount path allows you to specify where to make the volume available in the running container for a service. Anything your application reads and writes to the path will be written or read from the volume.
For example, using the path /data means any files in /data or subdirectories of /data will be written to or read from the volume. The container mount path is absolute, and must start from the container root (/).
Volume mount path
The volume mount path is optional and allows you to specify a directory on the volume to mount, rather than the volume root. The volume mount path is relative, and cannot start from root (/).
You can use this to persist data in multiple directories in a service on the same volume. Any data written or read from the container mount path will be written or read to the volume mount path.
| Container mount path | Volume mount path | Volume directory used | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
/data | - | / | The whole volume is mounted to the container path /data |
/data/config | config | config | The volume directory config is mounted to the container path /data/config |
/data/logs | logs | logs | The volume directory logs is mounted to the container path /data/logs |
Permissions
Ownership of persistent volumes will be given to the group specified in the Docker image, determined at build time. This may cause issues if your application attempts to read, write, or execute with a different user. You can designate the user and group the image will use in your Dockerfile with the command USER <user>:<group>.
To avoid permissions issues and to not overwrite any existing data from the image you should mount the volume only to the specific path(s) you require. For example if you mount a volume to /app/data your application may try to write data to that path and encounter permission errors, which may crash your application. If, in this case, you only need to persist data written to /app/data/logs, you should mount to that specific path instead. You can use volume mount paths to mount to multiple paths using the same volume.
If you are experiencing application issues with permissions, you can include a script as part of your application startup to run the chown command and change the directory to the required ownership and permissions: chown -R <user>:<group> /<container-mount-path>.
Alternatively you can set a custom entrypoint and command for the deployment, with the entrypoint as bash -c and the command as "chown -R <user>:<group> /<container-mount-path> && <default startup command>"
Scale a volume
To scale an attached volume, navigate to the volumes page of the service that has the volume attached. To scale a detached volume, navigate to any service's volumes page.
Select edit volume and open the storage dropdown to resize the volume. Volume storage cannot be scaled down.
Move or delete a volume
Volumes can be detached on the volumes page of the service they are currently linked to. Detaching a volume will redeploy any running containers in the service.
A volume must be detached from its current service before being attached to another. Attach a volume to another service by navigating to the detached section on the volumes page of the service you want to link it to and select on the volume to attach. Attaching a volume will redeploy any running containers in the service.
Volumes can be deleted by first detaching them, and then selecting delete .
Transfer data to and from a volume
You can transfer data to and from a persistent volume when it is mounted to a running service using commands like curl or wget. See transfer data to and from containers for more detail.